* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - StangBio
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
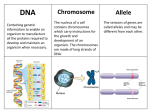
Allele Worksheet 1 Name: _______________ 1. Define each of these terms: Gene: __________________________________________________________________ Chromosome: ____________________________________________________________ Trait: __________________________________________________________________ Allele: __________________________________________________________________ Phenotype: ______________________________________________________________ Genotype: ______________________________________________________________ 2. For each of these genes, state which allele must be dominant and which must be recessive. Tt Dominant: ___ Recessive: ___ Gg Dominant: ___ Recessive: ___ Pp Dominant: ___ Recessive: ___ VV Dominant: ___ Recessive: ___ jj Dominant: ___ Recessive: ___ 3. State whether each of these genotypes is homozygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive. HH _______________________________ kk _______________________________ Uu _______________________________ vv _______________________________ Bb _______________________________ RR _______________________________ 4. For each of these genes, give the genotype that would be homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive. Y Homozygous dominant: ____ Heterozygous: ___ Homozygous recessive: ___ Q Homozygous dominant: ____ Heterozygous: ___ Homozygous recessive: ___ E Homozygous dominant: ____ Heterozygous: ___ Homozygous recessive: ___ M Homozygous dominant: ____ Heterozygous: ___ Homozygous recessive: ___ F Homozygous dominant: ____ Heterozygous: ___ Homozygous recessive: ___ 5. In each of these scenarios, give information about what the individual’s phenotype will be. a. With respect to the gene for coat color in mink, if the allele U produces a yellow coat and the allele u produces a brown coat, then an individual that is UU will have this coat color: _______. b. With respect to the gene for wing shape in house flies, if the allele I produces rounded wings and the allele i produces crooked wings, then an individual that is ii will have this wing shape: ________. c. With respect to the gene for eye color in Pacific salmon, if the allele P produces light eyes and the allele p produces dark eyes, then a salmon with the genotype Pp will have this phenotype: ___________. Allele Worksheet 1 Name: _______________ d. With respect to the gene for flipper length in bottlenose dolphins, if the allele T produces stunted non-functional flippers and the allele t produces normal flippers, then a dolphin with the genotype tt will have this phenotype: ________________. e. Huntington’s Disease in humans is caused by the manufacture of a damaged version of a protein called huntingtin. We will use M for the damaged version of the protein huntingtin and the allele m produces normal huntingtin. If a person has the genotype Mm, will they have Huntington’s Disease? ________ 6. Given information about these phenotypes, determine which alleles are which. a. In a group of mice, all individuals that are YY have long whiskers and all individuals that are yy have short whiskers. What is the allele for long whiskers? ____ What is the allele for short whiskers? ___ b. In a group of fish, all individuals that are OO have thin fins and all individuals that are oo have thick fins. What is the allele for thin fins? ____ What is the allele for thick fins? ___ c. In a group of dogs, all individuals that have the genotype Ee have floppy ears. What is the allele for floppy ears? ___ What is the allele for non-floppy ears? ___ d. We will use the alleles G and g for the gene for coat spots in rabbits. All rabbits that have one of these alleles have spots. No rabbits without spots have that allele, they only have the other allele. What is the allele for spots? ____ What is the allele for no spots? ____ e. We will use the alleles Q and q for the gene for fur smoothness in squirrels. All squirrels that are heterozygous have smooth fur, whereas only squirrels that are homozygous for one of those alleles have fluffy fur. Which is the allele for smooth fur? ___ Which is the allele for fluffy fur? ___ 7. In humans, who is heterozygous with respect to their biological sex? Men or women? Explain. _______________________________________________________________ 8. Suppose that 98% of the ferret population has smooth fur, and only 2% of the population has fluffy fur. Does this mean that the allele for smooth fur must be dominant? Explain. _______________________________________________________ 9. Complete this diagram by labeling each line with the relationship between the two concepts. Gene Chromosome Allele Trait