* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Make an Alien Lab
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
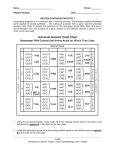
Name:_________________________________________ Determining the Traits of a “Mystery Organism” Through Protein Synthesis Introduction: Genes determine what characteristics an organism will have. Genes are segments of DNA molecules that are the instructions for building the proteins of the cell. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) is made from DNA and carries the instructions for how to make certain proteins. These instructions must be taken to the ribosomes where proteins are made. mRNA carries the instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes. Once at the ribosome, transfer RNA (tRNA) reads the message, gathers the necessary amino acids, and brings them to the ribosome. The amino acids are lined up, and connected together by peptide bonds to form a protein. This process is known as translation. In this lab, you will be creating a “mystery organism.” You must determine which proteins must be made to produce your mystery organism. You will be simulating the process of protein synthesis to determine the traits this organism will inherit. Your mystery organism belongs to the Animal Kingdom. It is made up of 6 different genes (A, B, C, D, E, and F). Each of these genes is responsible for a certain trait. Purpose: 1. 2. To see how the genes on a chromosome determine the characteristics of an organism. To simulate transcription and translation from a DNA template. Materials: Colored Pencils Paper Procedure: 1. Look at the boxes in the data table. You have been given the DNA sequence of 6 different genes that compose a mystery organism. From the DNA sequence given, determine the mRNA codons, the tRNA anticodons, the amino acid sequence, and the trait (protein) made by linking those amino acids. 2. To determine what traits your mystery animal has, fill in the boxes in the data table. 3. To determine the amino acid sequence, refer to the list below. This list contains all codons and their amino acid sequence. There are 20 different amino acids. A combination of many different amino acids composes different types of proteins. One amino acid is called for by one codon. A codon is a sequence of three nitrogen bases. There are 64 possible combinations of bases (codons), but only 20 amino acids. Several codons may be used to call for the same amino acid. Copyright © Science Stuff A Amino Acid Alanine Arginine Asparagine Aspartic Acid Cysteine Glutamic Acid Glutamine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine - Start Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine Stop Codons 4. Codons for this Amino Acids GCA, GCC, GCG, GCU AGA, AGG, CGA, CGC, CGG, CGU AAC, AAU GAC, GAU UGC, UGU GAA, GAG CAA, CAG GGA, GGC, GGG, GGU CAC, CAU AUA, AUC, AUU UUA, UUG, CUA, CUC, CUG, CUU AAA, AAG AUG UUC, UUU CCA, CCC, CCG, CCU AGC, AGU, UCA, UCC, UCG, UCU ACA, ACC, ACG, ACU UGG UAC, UAU GUA, GUC, GUG, GUU UAA, UAG, UGA To determine what traits are present in your mystery organism, refer to the table below. Use the amino acid sequences from your data table to determine what characteristic is being called for. AMINO ACID SEQUENCE TRAIT Alanine – Histidine – Lysine Proline – Serine – Phenylalanine – Glycine Tryptophan – Proline – Isoleucine Serine – Tryptophan – Lysine Cysteine – Alanine Arginine – Histidine – Threonine Histidine – Valine Alanine – Glycine – Proline – Serine Serine – Lysine Lysine – Leucine Tyrosine – Isoleucine – Aspartic Acid Proline – Alanine – Alanine Walks on four legs Freckles Walks upright on two legs Small purple ears Blue hair, very hairy Yellow eyes Very little red hair No Freckles Short orange nose Long red nose Blue eyes Green elephant ears Copyright © Science Stuff A Student Data Pages Data Table: GENE A DNA: ACC mRNA: GGT GENE B TAT Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: DNA: ACG mRNA: Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: GENE D DNA: GGA mRNA: CGA CGC GENE C DNA: TTT mRNA: Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: GENE E CGA Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: GENE F DNA: GGG AGG AAA CCC mRNA: DNA: GCT mRNA: Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: OBSERVATION QUESTIONS: 1. What part of this lab represented the process of transcription? 2. Where does transcription take place in the cell? 3. What part of the lab represented translation? 4. Where does translation take place? 5. Explain what a codon is. 6. Explain what an anticodon is. 7. Explain how a pearl necklace is like a protein. 8. Using colored pencils, draw your mystery organism on the back of this paper. A AAC GTG TGC