* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 432W9EX1
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
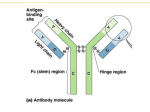
BI432 Immunology Exam #1 Winter, 1999 1 Name: 1. Indicate to which branch(es) of the immune system the following statements apply, using H for the humoral branch, CM for the cell-mediated branch, B for both branches and N for neither branch. a) Involves class I MHC molecules f) involves cytotoxic T cells b) responds to viral infections g) involves B cells c) involves T helper cells h) involves CD8+ cells d) involves processed antigen i) responds to extracellular bacterial e) most likely responds following an organ transplant infection j) kills virus-infected self cells 2. List the primary lymphoid organs and summarize the function of each in the immune response. 3. For each of the following statements, indicate whether it is true only of B cell epitopes (B), only of T cell epitopes (T), or both types of epitopes (BT) within a large antigen a) they ALWAYS consist of a linear sequence of amino acids b) they generally are located in the interior of a protein antigen c) they generally are located on the surface of a protein antigen d) they lose their immunogenicity when a protein antigen is subjected to heat denaturation e) immunodominant epitopes are determined in part by an individual’s MHC molecules f) they are present only in protein antigens g) multiple different epitopes may occur in the same antigen h) their immunogenicity may depend on the three dimensional structure of the antigen i) the immune response to them may be enhanced by Freund’s complete adjuvant. winword\immunol\432w9ex1 6/23/2017 4. Describe the products of treatment of an IgG with each of the following reagents: mercaptoethanol pepsin 5. Identify each of the indicated regions of the molecule in the figure immediately below. Label the location of the CDR with the letter “C”, the location of Ig fold #3 with the number 3, and the hinge region with the letter “H”. 6. According to the clonal selection theory, all the immuoglobulin molecules on a single B cell have the same antigenic specificity. Explain why the presence of both IgM and IgD on the same B cell does not violate the unispecificity implied by clonal selection. BI432 Immunology Exam #1 Winter, 1999 3 Name: 7. For each immunoglobulin isotype select the description(s) listed below (a-i) that are true about that isotype. Each description may be used once, more than once, or not at all; more than one description may apply to some isotypes. IgA: IgD: IgE: IgG: IgM: a) secreted form is a pentamer of the basic H2L2 unit b) binds to Fc receptors on mast cells c) multimeric forms have J chain d) present on the surface of mature, unprimed B cells e) the most abundant isotype in serum f) major antibody in secretions such as saliva, tears, and breast milk g) present on the surface of immature B cells h) plays primary role in protecting against pathogens that invade through the gut or respiratory mucosa i) multimeric forms may contain a secretory component 8. List, in increasing sensitivity, three qualitative immunoassays. 9. You perform an Ouchterlony assay in which the central well contains goat antiserum against the F(ab’)2 fragment of pooled mouse IgG and the surrounding wells (A-F) contain six different test antigens. The resulting precipitin pattern is shown below. Based on this pattern, indicate which well contains each of the following test antigens: a mixture of lambda heavy chains and kappa light chains a) Fab fragment from an IgG myeloma c) gamma heavy chains protein d) kappa light chains b) Fc fragment from IgG myeloma e) lambda light chain protein 10. Identify each of the cells, the types of Ig expressed, and the molecular events that occur at the steps in B-cell winword\immunol\432w9ex1 6/23/2017 development diagrammed in the following figure. 11. For each immunoglobulin heavy-chain or light-chain DNA, mRNA, of polypeptide described in the phrases a through g below, select the corresponding schematic diagram (1 to 9) from the figure below. BI432 Immunology Exam #1 Winter, 1999 5 Name: 12. List seven mechanisms that have been shown to generate antibody diversity in the mouse, and describe the manner in which any four of these mechanisms operate to produce antibody diversity. winword\immunol\432w9ex1 6/23/2017 BI432 Immunology Exam #1 Winter, 1999 7 Name: 1. Indicate to which branch(es) of the immune system the following statements apply, using H for the humoral branch, CM for the cell-mediated branch, B for both branches and N for neither branch. a) Involves class I MHC molecules f) involves cytotoxic T cells b) responds to viral infections g) involves B cells c) involves T helper cells h) involves CD8+ cells d) involves processed antigen i) responds to extracellular bacterial e) most likely responds following an infection organ transplant j) kills virus-infected self cells 2. List the secondary lymphoid organs and summarize the function of each in the immune response. 3. Complete the following table: CHARACTERISTIC B CELLS T CELLS Interaction with antigen binding of soluble antigen involvement of MHC molecules chemical nature of antigens epitope properties 4. Describe the products of treatment of an IgG with each of the following reagents: mercaptoethanol papain 5. Identify each of the indicated regions of the molecule in the figure immediately below. Label the location of winword\immunol\432w9ex1 6/23/2017 the CDR with the letter “C”, the location of Ig fold #3 with the number 3, and the hinge region with the letter “H”. 6. According to the clonal selection theory, all the immuoglobulin molecules on a single B cell have the same antigenic specificity. Explain why the presence of both IgM and IgD on the same B cell does not violate the unispecificity implied by clonal selection. BI432 Immunology Exam #1 Winter, 1999 9 Name: 7. For each immunoglobulin isotype select the description(s) listed below (a-i) that are true about that isotype. Each description may be used once, more than once, or not at all; more than one description may apply to some isotypes. Isotypes: IgA: IgD: IgE: IgG: IgM: a) secreted form is a pentamer of the basic H2L2 unit b) binds to Fc receptors on mast cells c) multimeric forms have J chain d) present on the surface of mature, unprimed B cells e) the most abundant isotype in serum f) major antibody in secretions such as saliva, tears, and breast milk g) present on the surface of immature B cells h) plays primary role in protecting against pathogens that invade through the gut or respiratory mucosa i) multimeric forms may contain a secretory component 8. List, in decreasing sensitivity, three quantitative immunoassays. 9. You perform an Ouchterlony assay in which the central well contains goat antiserum against the F(ab’)2 fragment of pooled mouse IgG and the surrounding wells (A-F) contain six different test antigens. The resulting precipitin pattern is shown below. Based on this pattern, indicate which well contains each of the following test antigens: a mixture of lambda heavy chains and kappa light chains a) Fab fragment from an IgG myeloma c) gamma heavy chains protein d) kappa light chains b) Fc fragment from IgG myeloma e) lambda light chain protein winword\immunol\432w9ex1 6/23/2017 10. Identify each of the cells, the types of Ig expressed, and the molecular events that occur at the steps in B-cell development diagrammed in the following figure. 11. For each immunoglobulin heavy-chain or light-chain DNA, mRNA, of polypeptide described in the phrases a through g below, select the corresponding schematic diagram (1 to 9) from the figure below. 12. List seven mechanisms that have been shown to generate antibody diversity in the mouse, and describe the manner in which any four of these mechanisms operate to produce antibody diversity.