* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CellReviewANS
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
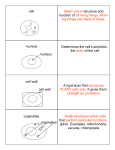
Cell Organelles In many cells, the structure that controls the cell's activities is the ....nucleus The organelle that makes energy available for the cell is ...the mitochondrion What is a vesicle? Distinct threadlike structures containing genetic information are .. small membrane-bound sac ...chromosomes What is the function of the What happens in the nuclear envelope? rough endoplasmic reticulum? ...a double membrane with pores that allow materials to ...ribosomes are found on move in and out of the cell the rough ER ...newly made proteins move from the ribosomes to the ER where they may be chemically modified What is the main function of the cell wall? What is the function of ribosomes? ...support and protection ...produce proteins following the genetic code from the nucleus What is chromatin? What is the function of the What are the two types of nucleolus? structures that make up the cytoplasm? ...granular material in the nucleus consists of DNA bound to protein Describe the role of the Golgi apparatus. ...enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins ...small dense region in the nucleus where the assembly of ribosomes begins microfilaments and microtubules What is the purpose of the vacuole? What is the difference between a rough and a smooth endoplasmic reticulum? What is the function of a lysosome? .......Store water and dissolved substances. ......smooth ER does not …these small organelles have ribosomes as the rough contain digestive enzymes ER does Prokaryotes or Eukaryotes What organisms are prokaryotes? What is the main characteristic of prokaryotes? If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is ...do not have a nucleus or cell organelles ..a eukaryote When did prokaryotes appear on earth? Animal cells and plant cells are (eukaryotes, prokaryotes). It is believed that mitochondria and chloroplasts are the descendents of …3.5 billion years ago …eukaryotes ...bacteria .....prokaryotes These were the first cells with internal compartments. (eukaryotes, prokaryotes). When did the eukaryotes first appear on the earth? Which are the smallest and simplest cells? (eukaryotes, prokaryotes). …1.5 billion years ago …prokaryotes How is the genetic material displayed in a prokaryote cell? Where is the DNA found in a eukaryote cell? What do bacteria have in place of an internal supporting skeleton? ......as a single, circular molecule of DNA in the cytoplasm ......in the nucleus .....strong cell wall What is the purpose of the capsule on some bacteria? What is the purpose of the flagella for bacteria? What unit of measurement is used in determining the size of cells? ......enables the bacteria to cling to almost anything ..... enable movement …eukaryotes ......µm (micrometer) CELL THEORY What is the contribution of Matthias Schleiden to the cell theory? What is the contribution of Theodor Schwann to the cell theory? What is the contribution of Rudolf Virchow to the cell theory? ...concluded that all plants are made of cells ... concluded that all animals are made of cells ... concluded that all cells come from preexisting cells Name the three parts of the cell theory A tissue is a group of What is the contribution of Robert Hooke to the cell theory? ...cell is the basic unit of structure of living organisms ...cells come from preexisting cells ...all living organisms are made of cells ...similar cells ...observed dead cells in cork ...named the "cell" The cell is the basic unit of Cells come from _____________ _______________ cells. of living things. All living organisms are made of _____________. .....structure ..... preexisting .......cells. How are cells like a whole organism? Why are small cells more efficient than large cells? What common boundary do all cells have? ....cells can carry out similar life processes as a whole organism .....Substances do not have to travel as far in a smaller cell than a larger cell thus taking less time to provide nutrients or to get rid of wastes. All cells have ___________ What is the purpose of the on which proteins are system of microfibers in made. the cell? ........ribosomes .......to provide support for the shape of the cell ...cell membrane All cells have _______ which provides instructions for making proteins. .......DNA Comparison of Plant and Animal cells Plants have an outer boundary that animal cells do not have. The cell wall in plants contains what polysaccharide? What takes up the main part of the plant cell? …cellulose …central vacuole The organelle in plants that carries out photosynthesis. What organelle do animal cells have that plant cells do not have? This is a _____cell. …chloroplast …centrioles This is a(an) ______ cell. What is the purpose of the central vacuole? …cell wall …animal …to store water and dissolved substances. …plant Name the three organelles that plants have and animal cells do not have. …chloroplasts, central vacuole, and cell wall What does B represent? What does A represent? What does C represent? .....central vacuole .....cell wall ......chloroplast What organelles in plant cells have double membranes? What other organisms besides plants have chloroplasts? What organelle in plants presses against the cell wall making the cell rigid? ...mitochondria and chloroplasts ......central vacuole .....algae Microscopes How is the image formed for compound light microscope? How is an image formed for electron microscopes? What adjustment knob is used for focusing while using the high power objective? .....light passes through one or more lenses ......a beam of electrons is used .......fine adjustment knob What adjustment knob is used for focusing while using the low power objective? What is the purpose of the diaphragm on the compound light microscope? Which kind of microscope must view the specimen in a vacuum? ......electron microscope .......coarse adjustment knob .......adjustment of the amount of light through the microscope Specimens may be magnified over 200,000 times with this microscope. What is the maximum magnification that is known for the compound light microscope? .......electron microscope ........2,000 times Explain how to calculate total magnification for a compound light microscope. What is the purpose of the revolving nosepiece on the compound light microscope? Which microscope can produce images that are three-dimensional? .........changes the power of the magnification .......electron What is the purpose of the stage on the microscope? What is the definition of microscope magnification? Why can only dead cells be observed under an electron microscope? ........for the placement of the microscope slide .......the ability to make an image appear larger than its actual size .......the cells must be viewed in a vacuum ......multiply the power of the eyepiece lens and the objective lens What is meant by resolution for microscopes? .........measurement of the clarity of the microscope image