* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HAPPY WEDNESDAY
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
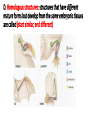
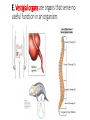
C3 Computer HAPPY FRIDAY Bellwork: How many green stars do you see on each square? Black stars on each square? What is this an example of? Peppered moths are eaten by birds. The moth color varies from light to dark. Light colored moths can blend in with a nearby species of tree. In the 1800s factories released large amounts of soot, which changed the tree color, so the birds were able to more easily find the lighter moths instead of the darker moths. Collect Today Page 88 – Evolution Bean Lab Graph Page 91 – Anatomical Homologies Coloring Page Assigned Page 90 – Fossil Dating (Monday) Page 86 – Notecard Definitions (Monday) Evolution Quiz (Monday) Most Missed Quiz – Genetics (Wednesday) Late Family Tree Project– Include Rubric and Punnett (-50 points) Page 87 – Natural Selection Video Guide (-30%) Squares Unit 6 – Evolution Definitions Due Monday (1/11/16) All Parts Due Friday (1/15/16) 1. Adaptation 13.Evolution 2. Anatomical Homologies 14.Fitness 3. Ancestry 15.Fossil Record 4. Artificial Selection 16.Founder Effect 5. Biodiversity 17.Gene Flow 6. Biogeography 18.Gene Pool 7. Bottleneck Effect 19.Genetic Drift 8. Charles Darwin 20.Genetic Variation 9. Common Descent 21.Gradualism 10.Developmental Homologies 22.Homologous Structures 11.Disruptive Selection (Graph) 23.Homology 12.Directional Selection (Graph)24.Limiting Factor PG 86 25.Migration 26.Molecular Homologies 27.Natural Selection 28.Non-Random Mating 29.Overpopulation 30.Recombination 31.Reproductive Success 32.Speciation 33.Stabilizing Selection (Graph) 34.Stasis 35.Theory 36.Vestigial Structure II. How Evolution Works A. Artificial selection: selection by humans for breeding of useful traits 1. The struggle for existence is competition among members of a species for food, living space, and the other necessities of life. 2. High birth rates and a shortage of life’s basic needs eventually forces organisms into a competition for resources. B. Fitness: the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce 1. Fitness is the result of adaptations. 2. Adaptation: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival. a. Successful adaptations: - enable organisms to become better suited to their environment - increase an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce. Humans have thousands of adaptations: large brain, opposable thumbs, excellent sensory organs, light, strong skeleton, etc. C. Natural selection: the process by which individuals with characteristics that are not well suited to their environment either die or leave few offspring. 1. Also referred to as survival of the fittest. 2. It is not seen directly, but only observed as changes in a population over a long time. 3. Zombieland: The Rules Essential Question PG 89 What evidence supports the theory of evolution? Standard B.7C - Analyze and evaluate how natural selection produces change in populations, not individuals. B.7E - Analyze and evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and to the development of diversity in and among species. A. Descent with modification: a principle that says each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time. 1. It implies that all living organisms are related 2. Also known as common descent. 3. States all species were derived from common ancestors. B. Darwin found evidence in: 1. the fossil record 2. the geographical distribution of living species (Biogeography) 3. homologous structures of living organisms 4. similarities in early development, or embryology. PG 90 Activity break – DEMO Essential Question What evidence supports the theory of evolution? C. Scientists use the fossil record to help determine evolutionary changes. By comparing fossils from older rock layers with fossils from younger layers, scientists could document the fact that life on Earth has changed over time. Researchers have discovered many hundreds of transitional fossils that document various intermediate stages in the evolution of modern species from organisms that are now extinct. Gaps remain in the fossil record. These gaps do not indicate weaknesses in the theory of evolution itself. Rather, they point out uncertainties in our understanding of exactly how some species evolved. PG 91 Color Break Essential Question What evidence supports the theory of evolution? D. Homologous structures: structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues are called (start similar, end different) E. Vestigial organs are organs that serve no useful function in an organism. Something Important to Know: Theory: a well-supported scientific explanation that is subject to change. Law: a scientific fact. Evolution is a theory. Evolution is often called “the grand unifying theory of biology.” Evolutionary theory continues to change as new data are gathered and new ways of thinking arise.