* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each)
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
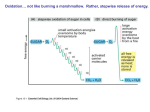
Page 1 Code Number ____________ PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each) Pick up your number 2 pencil and your scantron sheet and get rolling! Put your NAME, SUID#, and TEST CODE NUMBER on both sides of the scantron immediately. Please bubble in 'A' if the statement is TRUE and 'B' if the statement is FALSE. Remember to be careful when bubbling in your answer. ERASE COMPLETELY. 1. Both amino acids and sugars are linked into macromolecules via condensation reactions, in which a molecule of water is generated. 2. In living organisms, the majority of proteins found exist in only one isomeric form. 3. Within a single protein, both alpha helices and beta sheets can be present. 4. Noncovalent bonds are the main determinant of protein tertiary structure. 5. According to the lock and key model of a substrate binding to an enzyme, no confirmational changes in the substrate binding site occur. 6. If an enzyme's Km is very low, it indicates that the enzyme-substrate binding affinity is very weak. 7. Two labs measuring the rate of product formation for a reaction, but using different amounts of the same enzyme, will calculate different Vmax values. 8. Phospholipids spontaneously aggregate into micelle, surface monolayer, or bilayer membrane arrangements. 9. The nucleus is surrounded by two membrane bilayers. 10. The nuclear import receptor remains permanently bound to the imported protein after it has passed into the nucleus. 11. The Golgi apparatus is a site for post-translational protein modification. 12. Having many intermediates in the oxidation of glucose allows a more efficient transfer of energy than burning glucose in only one step. 13. All glucose in the bloodstream is immediately broken down after entering the cell, through glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 14. Kinesins and dyneins move along microtubules using the energy from hydrolyzing ATP. 15. Large hydrophilic primary messengers bind to intracellular receptors in order to regulate gene expression. Page 2 Code Number ____________ 16. Acetylcholine can cause opposite effects in different cells. 17. Primary messengers binding to G-protein-linked receptors never contact the cytosol. 18. All behavior is a result of external stimuli and reinforcement, thus allowing all behavior to be manipulated and modified. 19. Male sticklebacks responding to red mail trucks demonstrated the ability of a key stimulus to trigger the fixed action patterns of territoriality. 20. Vaccines rely on the proper functioning of immunological memory to confer protective immunity on the host. 21. Heavy chains of immunoglobulins have variable regions, while light chains do not. Page 3 Code Number ____________ PART 2: MATCHING (1 point each) Answer the following matching questions on your scantron. Remember to choose the BEST answer for each question. Match the following descriptions with the most appropriate amino acid from the list. Use only one amino acid for each answer. Each amino acid on the list may be used more than once or not at all. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) tyrosine serine glutamic acid arginine proline 22. positively charged 23. negatively charged 24. nonpolar 25. likely to cause "kinks" between protein secondary structures 26. phosphorylated by PKCs 27. phosphorylated by the main class of enzyme-linked receptors Match the following descriptions with the most appropriate cytoskeleton filament. (a) (b) (c) (d) Intermediate filaments Microtubules Actin filaments Equally true of all cytoskeleton filaments 28. Smallest in diameter (7 nm). 29. No structural polarity. 30. Primary filament responsible for movement of cells. 31. Usually grow from nucleating sites of gamma-tubulin. 32. Make up the mitotic spindle. 33. Almost all of its monomer is associated into filaments in the cell. 34. Made of protein. 35. Colchicine prevents its polymerization. Page 4 Code Number ____________ Indicate to which branch(es) of the immune system the following statements apply. (a) Humoral (b) Cell-mediated (c) Both humoral and cell-mediated 36. Involves class I MHC molecules. 37. Involves T-helper cells. 38. Involves T-cytotoxic cells. 39. Kills virus-infected self-cells Match the following immunoglobulins with their most accurate description from the list below. Note: each description can only be used ONCE. 40. IgA 41. IgD 42. IgE 43. IgG 44. IgM (a) In allergic responses, binds to receptors on mast cells. (b) The first serum antibody made in a primary immune response. (c) Endocytosed by placenta and released into fetal circulation. (d) Major antibody in secretions such as saliva, tears, and breast milk. (e) Present on the surface of mature, unprimed B cells. Page 5 Code Number ____________ PART 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE (2 points each) Move to the second column of your scantron answer sheet and begin bubbling in your answers to these questions in row 51. Remember to choose the BEST answer for each question. Again, be careful when you bubble in your answer. ERASE COMPLETELY. 51. Which of the following is a normal width range for a eukaryotic cell, for example, a heart cell? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 0.1 nm 10 nm 0.1 µm 10 µm 0.1 mm 52. Which of the following phospholipids is the MOST ABUNDANT in the cell membrane? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Phosphotidylinositol phosphates Phosphotidylserine Phosphotidylcholine Glycolipids Phosphotidylethanolamine 53. Which of the following is NOT a function of the cell membrane? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Exchange of molecules (import/export). Allow and regulate lateral mobility of proteins. Capacity for movement and expansion. Signal transduction. All of the above are functions of the cell membrane. 54. In an experiment, attaching a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) to keratin results in translocation of keratin into the nucleus. This experiment best demonstrates that the NLS is ___________________. (a) (b) (c) (d) Sufficient to cause translocation of a protein into the nucleus. Necessary to cause translocation of a protein into the nucleus. Correlated with translocation of a protein into the nucleus. Both A and B are demonstrated by this experiment. Page 6 Code Number ____________ 55. Into which of the following organelles does transport of a protein occur while the protein undergoes translation? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Mitochondria 56. Which of the following is NOT a product of the citric acid cycle? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) pyruvate carbon dioxide NADH FADH2 GTP 57. During electron transfer in the respiratory chain, the proton concentration in between the inner and outer membrane of the mitochondria is ________________ the proton concentration of the mitochondrial matrix. (a) (b) (c) (d) the same as higher than lower than cannot be determined 58. Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is FALSE? (a) (b) (c) (d) Muscles are made up of myofibrils, which are made of sarcomeres. Ion channel-linked receptors are involved in muscle contraction. In a muscle contraction, actin is the motor that slides myosin II filaments past each other. Muscle contraction uses oxygen because muscle contraction needs the ATP generated by oxidative phosphorylation. (e) Mitochondria in muscle cells have more cristae than mitochondria have in other cells. 59. Tolerance to pain killers in patients with chronic pain can be attributed to what phenomenon? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) receptor agonist activity receptor antagonist activity receptor desensitization allosteric inhibition A and B only Page 7 Code Number ____________ 60. Which of the following is/are true statement(s) regarding protein phosphorylation? I. Phosphatases add phosphate groups to amino acids. II. Phosphate groups can be added only to serine, threonine and tyrosine. III. Phosphorylation can turn a protein either on or off. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) I only II only I and II only II and III only I, II and III only 61. Which of the following is/are true statement(s) regarding Protein Kinase A? I. cAMP binds to PKA's catalytic subunit leading to its dissociation from the regulatory subunit. II. One of the short-term effects of phosphorylation by PKA is the desensitization of receptors. III. One of the long-term effects of phosphorylation by PKA is a change in gene expression. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) I only II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III only 62. Which of the following statements regarding imprinting is FALSE: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Occurs during a critical/sensitive time period during development. Can influence sexual preferences of an imprinted animal later in life. The strength of imprinting varies based on age at which imprinting occurs. Auditory imprinting does not occur. All of the above statements are TRUE statements regarding imprinting. 63. Which of the following statements about the biological basis of behavior is FALSE? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Changes in hormone levels can alter behavior. Changes in behavior can alter hormone levels of an animal, in its lifetime. Changes in behavior can alter the hormone profile of a species over evolutionary time. Behavioral patterns can be inherited. All of the above are TRUE statements. Page 8 Code Number ____________ PART 4: SHORT ANSWER Please put away your scantron and take out a black or blue PEN. NO REGRADES will be given for answers written in pencil. Be sure to put your final answers on the lines and inside the boxes for each question. Answers that exceed the allotted space will not be graded. PROBLEM #1 (15 points) A. (4 points) The ∆G for the following reaction is +4.5. Draw a free energy diagram for this reaction. Label the ∆G, the activation energy, and the specific reactants and products for the forward reaction. inositol trisphosphate + diacylglycerol [ IP3 + DAG phosphatidylinositol PIP2 ] Free Energy Reaction progress in time B. (1 point) The enzyme phospholipase C is added to this reaction. Use a DOTTED LINE to depict the altered free energy diagram on the same graph above. C. (2 points) Phospholipase C (circle one) INCREASES / DECREASES / MAINTAINS the time it takes for the reaction to reach equilibrium, and (circle one) DECREASES / MAINTAINS INCREASES / the equilibrium product to reactant ratio. D. (1 point) Apa decides she wants to study phospholipase C’s ability to catalyze the formation of IP3. She obtains the following graph: Page 9 Code Number ____________ phosphatidylinositol inositol trisphosphate + diacylglycerol [ PIP2 IP3 + DAG ] What is phospholipase C's Km? Graphically show your work. ________________ E. (2 points) Vivian adds a competitive inhibitor to PIP2 into this reaction. This will (circle one) RAISE / LOWER / MAINTAIN the Km, and (circle one) RAISE / LOWER / MAINTAIN the Vmax of phospholipase C’s enzyme kinetics curve. F. (2 points) In another series of experiments, Janet adds a noncompetitive inhibitor to PIP2 into this reaction. Use a DOTTED LINE to depict the altered enzyme kinetics curve on the above graph. G. (2 points) The membrane phospholipid involved in the equation in Part D is depicted below. Label the parts of this phospholipid. Page 10 Code Number ____________ A. ________________________ B. __________________________ C. ________________________ D. __________________________ H. (1 point) Label the cytoplasmic and extracellular environments in this picture. E. _______________________ F. ____________________________ Page 11 Code Number ____________ PROBLEM #2 (13 points) A. (4 points) For each one of the following processes, write on the line where EXACTLY the process occurs. Please be PRECISE. 1. Glycolysis 2. Pyruvate Oxidation 3. Citric Acid Cycle 4. Electron Transport Chain For each one of the following scenarios place an "X" by the effects which will occur as a result of the problem described. B. (4 points) Vivian is swimming a 50-meter freestyle in the PAC-10 championships. She is trying to beat her best time of 25 seconds. So, she is moving fast! Place an "X" by the events that will occur in her muscle cells, which are not receiving oxygen. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ glycolysis occurs pyruvate oxidation occurs TCA cycle occurs electron transport chain occurs NAD+ is regenerated during the electron transport chain ______ NADH is regenerated during the electron transport chain ______ NAD+ is regenerated during lactic acid formation ______ NADH is regenerated during lactic acid formation ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ pyruvate converts to lactic acid 2 net ATP generated / glucose pH in cells decreases pH in cells increases acetyl CoA serves as final electron acceptor ______ O2 serves as final electron acceptor ______ efficient generation of ATP from glucose ______ inefficient generation of ATP from glucose Page 12 Code Number ____________ C. (3 points) Vivian's friend, Fido, unfortunately is not feeling as energetic as Vivian. Dr. Sohoni has been examining Fido and has discovered that Fido accidentally ate some poison that is inhibiting his ATP synthase. Protons are being blocked from traveling through the synthase. Place an "X" by the immediate events that will occur in his cells. ______ glycolysis occurs ______ pyruvate oxidation occurs ______ TCA cycle occurs ______ pyruvate converts to lactic acid ______ O2 serves as final electron acceptor ______ acetyl CoA serves as final electron acceptor + ______ NAD regenerates during the electron ______ pH in mitochondrial intermembrane transport chain space increases ______ NADH regenerates during the electron ______ pH in mitochondrial intermembrane transport chain space decreases ______ NAD+ regenerates during lactic acid ______ pH in mitochondrial intermembrane formation space remains constant D. (2 points) Fido's friend, Toto, is doing even worse than Fido. Dr. Chinosornvatana examined Toto and discovered that Toto's hexokinase is not functioning properly. Hexokinase is the enzyme that phosphorylates glucose as soon as glucose enters the cell and is the catalyst for the first step of the glycolysis pathway. Place an "X" by the events that will occur in Toto's affected cells. ______ ______ ______ ______ glycolysis occurs pyruvate oxidation occurs fats broken down to produce ATP acetyl CoA serves as final electron acceptor ______ pyruvate converts to lactic acid ______ 2 net ATP generated / glucose ______ proteins broken down to produce ATP ______ there will be absolutely no ATP generated in the cell Page 13 Code Number ____________ PROBLEM #3 (22 points) A. (8 points) The following flow chart depicts two signaling cascades you have studied. Please fill in the blanks for the sequence of events. BE SPECIFIC. Signal Hormone Receptor Coupling Protein G-protein Effector Second Messenger Precursor Second Messenger(s) Target Enzyme PKA Ca2+ PKC B. (1 point) In the above flow chart, circle the second messenger that is hydrophobic. C. (1 point) From the above flow chart, the calcium ions listed are released by which organelle? ______________________________ Page 14 Code Number ____________ D. (3 points) Low concentrations of primary messengers can produce surprisingly large-scale effects within a cell. Identify two steps within the G-protein-linked receptor pathway in which amplification occurs and briefly explain how. 1. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ E. (9 points) The following table presents features from one or more of signaling cascades identified by a key kinase in that cascade. For each characteristic, please circle all the pathways it is associated with. For each feature, there is at least one correct answer. (PKA = Protein Kinase A, PKC = Protein Kinase C, RTK = Receptor Tyrosine Kinase). 1. Hydrophilic primary messenger PKA PKC RTK 2. Alpha helices in receptor transmembrane structure PKA PKC RTK 3. 7-pass receptor transmembrane structure PKA PKC RTK 4. Ras protein PKA PKC RTK 5. RACKs for localization PKA PKC RTK 6. Catalytic subunit separates from regulatory subunit when activated PKA PKC RTK Page 15 Code Number ____________ PROBLEM #4 (25 points) A. (1 point) Immunity has both nonspecific and specific components. Inflammatory barriers and anatomic barriers such as skin are examples of the (circle one) NONSPECIFIC / SPECIFIC component. B. (3 points) Specific immunity displays four hallmark characteristics, one of which being immunologic memory. LIST 3 other hallmark characteristics: 1. 2. 3. C. (2 points) The immune system generates specific B and T cells to bind individual antigens that infect an organism. B cells mature in the T cells mature in the generate a diversity of antibodies occurs in (circle one) B / Gene rearrangement to T cells. Upon encountering an antigen that binds to the membrane bound antibody, this cell divides rapidly, generating cells that secrete antibody called . D. (3 points) T cell receptors recognize antigen bound to MHC molecules. (Circle one) MHC CLASS I / MHC CLASS II molecules are expressed on all nucleated cells in the body. Thelper cells display (circle one) CD4 / CD8, and are activated by binding with antigen complexed with MHC II. T-helper cells secrete to signal primarily three other cell types using ENDOCRINE/ PARACRINE/ CONTACTDEPENDENT signaling. List two of the three cell types the receive these signals from Thelper cells: Page 16 Code Number ____________ . E. (6 points) The diagram below shows an antibody molecule. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. 1. (3 points) In the answer box provided, match the following terms with the letter that BEST describes them. Term Fab region Fc region Heavy chain Light chain Beta strand Likely location of proline Letter 2. (1 point) What bond is labeled by letter E? 3. (1 point) This bond is a (circle one) INTERMOLECULAR / INTRAMOLECULAR bond. 4. (1 point) Which amino acid is responsible for forming the S-S bonds labeled by the letter E in the antibody molecule (Three letter abbreviation or full name acceptable) ? 5. (1 point) Label the N and C terminus of each polypeptide chain of the antibody molecule on the right figure.