* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Notes
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
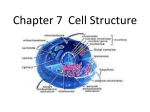
Chapter 3 Notes-Section 1 All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells come in many sizes and shapes and have many functions -were not discovered until the invention of the microscope. Robert Hooke-first person to identify, describe and use the term “cells” -he used cork material from trees, as saw many small boxes. -he used the term cells because it means “tiny rooms: -he later looked at living plant cells, noticing “juice” in living cells. -he looked at other materials as well (fungi, feathers, scales) Anton van Leewenhoek-looked at pond scum, water from his rain barrel, etc. -noticed what he called tiny animals, or “animalcules” -Today these single celled organisms are known as Protists. -he looked at all kinds of animal cells -first to see bacteria and yeast cells Cell Theory With the work of these scientists and several others the cell theory was developed. Schleiden-all plants are made of cells Schwann-all animals are made of cells Virchow-new cells can only come from existing cells. The Cell Theory states: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells Cell Size Most are too small to be seen without a microscope. Organisms that lay eggs are the only large cells. Why can’t cells be large?” Cells take in food and get rid of wastes through their outer surface. If they grow too large, they need more food and make more waste than can move across the outer surface. The volume of the cell’s size inside increases at a faster rate than the cell’s surface. The cell can’t get enough food in and waste out to handle this increase. What do Cell’s have in common? *All are surrounded by a protective cover called Cell membrane. -it acts like a barrier (thin and flexible) -it controls what goes in and out *All have Cytoplasm- a gel-like fluid and almost all other content inside of the cell membrane *Organelles-structures that perform specific tasks inside of the cell *Genetic Material-(DNA) material that carries information needed to make new cells and materials. It passes from parent to offspring In most cells DNA is found in a nucleus. In others, like bacteria, it is not. Two Kinds of Cells 1. Prokaryotes-have no nucleus, do have membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA Examples: Eubacteria (bacteria) world’s smallest cells; found everywhere; also have a strong cell wall to keep shape Archaebacteria: Similar to eubacteria except their ribosomes, cell walls, and membranes are different; they also live in places where other organisms could not live like harsh environments like swamps, volcanic vents, very salty, etc.. (Extremophiles) 2. Eukaryotes-larger cells, have a nucleus with DNA, membrane bound organelles that perform specific jobs; some are single celled (protists) but many are multicellular(you, fungi, plants)