* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Summary Questions
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
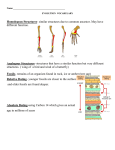
Evolution Summary 2015 1) List the evidence that supports Darwin’s idea of descent with modification. Give an example of each. a) Fossils - Body Structures and Changes in Organisms b) Homologous Structures - Same Origin, Different Use c) Vestigial Organs - Structures that are no longer used, but still there d) Biochemistry and Genetics - Comparing Organic Compounds e) Embryological Development - Comparing Development before Birth f) Common Ancestry - Using all of the Above to Compare Organisms The best evidence is to combine ALL of the evidence to get a better idea of the relationships among organisms. Embryology, Biochemistry, and Genetics are the newest, and in most cases, the best evidence that we have. 2) How do analogous and homologous structures support the idea of Natural Selection leading to Evolution? Natural selection is survival of the best adapted (Def: a change or adjustment for a new purpose or conditions) Evolution is Natural Selection, and the best adapted reproduce and pass those “adapted” traits on. Homologous structures: SAME Origin, DIFFERENT Use (Ex. Bones in arms of humans, Birds, & Whales) Natural Selection would favor the best adapted. The bones in the arm of an animal would change because the PRE-whale was swimming in water. Those animals with better adapted “flippers”, would survive and pass on the better “flipper” traits to their offspring. The “flippers” would continue to change, or Evolve into a whale. Evolution modifies existing structures. So the bones in one organism are use to make flippers. The same bones in another organism are use to make legs because that organism needs to run, not swim. Analogous structures: DIFFERENT Origin, SAME Use (Ex. Wings of Birds and Insects) Natural Selection would favor the best adapted. The bones in the arm of an animal would change because the PRE-Bird was flying or gliding in air. Those animals with better adapted “wings”, would survive and pass on the better “wing” traits to their offspring. The “wings” would continue to change, or Evolve into a bird. Evolution modified the existing bones to make wings. However, Insects DO NOT have bones. So instead, Evolution modified DIFFERENT structures in the insect to make wings. Because flying is a Very Good adaptation, it evolved in many different species from many different structures that all do the same thing: Allow an organism to fly. 3) Explain why Darwin’s Finches (there are 14 of them) are examples of Divergent Evolution. Divergent Evolution is ONE (Common Ancestor) evolving into two or more new species. There was ONE ancestral finch species that landed on the Galapagos Islands millions of years ago. Since the food supply and habitat is different on each island, finches that landed on one island, adapted and evolved for the conditions on that island. Finches that landed on other islands, evolved for the conditions on those islands. So from one species of finch, fourteen (14) new species evolved to survive in different conditions on different islands. 4) Explain why a Dolphin (Mammal) and a Tuna (Fish) are examples of Convergent Evolution. Analogous structures: DIFFERENT Origin, SAME Use (Ex. Fins and Body of Dolphins and Tuna) Convergent Evolution is different organisms, due to evolution, arriving at the same structures. Water is water. Any animal that swims long distances and has to catch food will evolve a body, fins, and other structures to do that. If certain shapes and structures work, all organisms will evolve them. So Dolphins and Tuna have analogous structures (and Convergent Evolution happened) because that is what works best in water. 5) Explain why DNA and the three (3) other types of organic molecules are evidence of common ancestry. If we all use the same organic compounds (Lipids, Nucleic Acids, Proteins, Carbohydrates) then we ALL inherited them from a common ancestor. If the first organisms used them, and they are still around, it shows common ancestry. The same is true of DNA. All organisms use it to store information, so it shows that we ALL inherited from a distant common ancestor. 6) Why did some species, such as humans, survive while other species, such as the Tiktaalik, go extinct? If a species CAN adapt, and evolve to the change it will. If the change is too sudden, or too extreme, or the organism does not have the structures to adapt, then it cannot evolve, and so it goes extinct. If another organism is better adapted, it will survive and the other organism will go extinct. Better amphibian-like organisms than Tiktaalik evolved and survived. And so far, no other Human-like organism has challenged us.