* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fall07_Exam3
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Early 2014 North American cold wave wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
North Report wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
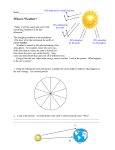
ATMO 336 – Section 001 Exam 3 – Fall 2007 Name__________________________ Multiple Choice Section (2.5 points each) 1. The climate of a particular region on Earth is fully described by the average temperature and average precipitation (called “normals”) compiled over a 30-year period. (a) True (b) False 2. We have had a warm November in Tucson. Record high temperatures were set on November 5, 7, 18, and 19. These facts prove that global warming is taking hold and that temperatures will get even warmer if we continue to pollute the atmosphere with greenhouse gases. (a) True (b) False 3. Radiation energy from the Sun that strikes the top of Earth’s atmosphere can either be absorbed or scattered (reflected) away to outer space. Which of the following is the most correct breakdown for what happens to radiation energy from the Sun that strikes the top of our atmosphere? (a) 50% is scattered away; 50% is absorbed by ground surface and oceans; 0% is absorbed by the atmosphere (b) 30% is scattered away; 50% is absorbed by ground surface and oceans; 20% is absorbed by the atmosphere (c) 30% is scattered away; 35% is absorbed by the ground surface and oceans; 35% is absorbed by the atmosphere (d) 20% is scattered away; 80% is absorbed by the ground surface and oceans; 0% is absorbed by the atmosphere 4. Most of the photons emitted from the surface of the Earth (land and oceans) __________ . (a) are absorbed by atmospheric gases and clouds (b) are reflected back to the surface by atmospheric gases and clouds (c) go directly off into outer space 5. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has _________ since 1750. (a) increased by about 10% (c) approximately doubled (b) increased by about 35% (d) more than tripled 6. Rice cultivation and cattle raising are significant anthropogenic sources (due to human activities) for the greenhouse gas _________ . (a) CO2 (Carbon dioxide) (c) CH4 (Methane) (b) N2O (Nitrous oxide) (d) CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) 7. Too bad the US did not agree to and sign the Kyoto Protocol, which was aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, because if we had, the world would not be faced with the problem of global warming. (a) True (b) False 8. This feedback mechanism (described in lecture) is largely responsible for amplifying the overall global average temperature increase predicted by climate models after greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere are increased. (a) Snow/Ice albedo (reflectance) feedback (c) Water vapor feedback (b) Carbon dioxide fertilization feedback (d) Cloud emission feedback For Questions 9 and 10 The amount of carbon dioxide that is stored in the ocean surface waters depends on two things: A. The ocean surface temperature. As the ocean surface temperature goes up, the amount of CO2 dissolved in the oceans at equilibrium goes down. In other words, as the ocean surface temperature warms, some of the dissolved CO2 in the ocean is released to the air. B. The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. As the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere goes up, the amount of CO2 dissolved in the oceans at equilibrium goes up. In other words, as CO2 is added to the atmosphere, some of it dissolves in the oceans. Consider the following two steps as the beginning of a climate feedback cycle: Humans add CO2 to the atmosphere As a result, surface temperatures (land and ocean) begin to increase 9. Continuing with this feedback cycle, Process (A) above would act as a _____ feedback. (a) positive (b) negative 10. Continuing with this feedback cycle, Process (B) above would act as a ______ feedback. (a) positive (b) negative 11. Clouds have ________ influence on the surface temperature of the Earth (a) a warming (c) both a warming and a cooling (b) a cooling (d) neither a warming nor a cooling 12. We rely on computer models of global climate to predict what will happen as greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere increase. Which statement about predictions of climate models is most correct? (a) Nearly all models predict that global average temperature will increase, but they differ in exactly how much warming will occur. (b) The model predictions are all over the place with respect to global average surface temperature – some models predict that global average temperature will increase, some models predict that global average temperature will decrease, and some models predict no change in global average temperature 13. According to most climate models, if the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere were instantly doubled from what it was before the Industrial Revolution and then left unchanged, the average surface temperature of the Earth would __________ . (a) warm by about 30 C over a period of a few years (b) warm by about 30 C over a period of about 100 years (c) warm by about 3 C over a period of a few years (d) warm by about 3 C over a period of about 100 years 14. Assuming that global average temperature continues to rise, the one side effect (of the choices given) that we are most certain about is ______________ . (a) the number of hurricanes will increase (b) farming production in the U.S. will decline (too hot), but farming production in Canada and Russia will increase (longer growing season). (c) tropical diseases will spread further north and south away from the equator (d) sea level will rise 15. The most recent IPCC report (released in 2007) concludes with ___ percent certainty that most of the recent increase in global average temperature has been caused by anthropogenic increases in greenhouse gases. (a) 0 (b) 50 (c) 90 (d) 100 16. A land bridge connecting Russia with Alaska formed during an ________ when sea levels were ________ . (a) interglatial warm period ; much lower than today (b) interglatial warm period ; much higher than today (c) ice age ; much lower than today (d) ice age ; much higher than today 17. The most recent ice age cycles on Earth (over the last two million years) were most likely triggered by ___________ . (a) changes in the positions of the continents (b) decreases in the energy output of the Sun (c) variations in Earth's orbit around the Sun (d) volcanic eruptions which eject massive amounts of aerosols into the atmosphere 18. This was probably the warmest period in the last 15,000 years. During this period, the global average temperature was probably warmer than it is today. (a) Holocene Maximum (c) Little Ice Age (b) Medieval Warm Period (d) Younger Dryas 19. Global average surface temperatures from 1990 through today are warmer than at any other time since 1860. This statement is _______________ . (a) almost certainly true (b) believed to be true by many people, but it is difficult to back up with evidence (c) not true; It is a scare tactic used by those who warn about the evils of modern society. 20. From about 1910-1940, the measured global average surface temperature _________ ; this period _______ provide good evidence that the rise in global average temperature since 1900 is directly caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. (a) decreased significantly ; does not (b) decreased significantly ; does (c) increased slightly ; does (d) increased slightly ; does not 21. From about 1940-1980, the global average surface temperature __________ ; one possible explanation for this temperature trend is the production of sulfate aerosols from ________. (a) decreased significantly ; higher ocean temperatures (b) decreased significantly ; coal burning (c) increased slightly ; coal burning (d) increased slightly ; higher ocean temperatures 22. An overwhelming majority of atmospheric scientists believe that most of the recent rise in global average surface temperature is directly caused by human activities … and if we continue to emit greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, we can expect future catastrophe for inhabitants of the Earth. (a) True (b) False 23. On May 1, which of the following locations will have the greatest number of daylight hours? (a) Perth, Australia (32˚ South latitude) (b) Tucson, Arizona (32˚ North latitude) (c) McMurdo Station, Antarctica (77˚ South latitude) (d) Galapagos Islands (0˚ latitude, Equator) 24. In Tucson (32 North latitude), the noon-time sun is _________ . (a) south of straight up everyday of the year (b) north of straight up everyday of the year (c) north of straight up from March 21 – September 21 and south of straight up from September 21 – March 21 (d) south of straight up from March 21 – September 21 and north of straight up from September 21 – March 21 25. Which large-scale feature in the Earth’s precipitation pattern best explains the climate of Tucson? In other words, Tucson is located in the region, named the __________ . (a) Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) (c) Polar front (b) Subtropical high (d) Polar high For Questions 26 and 27 Wichita, Kansas and San Francisco, California are both located at 37.6 north latitude. Wichita is located near the middle of the North American continent, while San Francisco is located on the Pacific Ocean coast. For January, the average high temperatures of the two cities are 56 F and 40 F. For July, the average high temperatures are 93 F and 72 F. 26. Which location has the more intense sunshine and greater number of daylight hours during the month of July? (Ignore differences that may be due to cloud cover or elevation) (a) Wichita (b) San Francisco (c) Both cities should have about the same solar intensity and number of daylight hours 27. Which average high temperatures are associated with Wichita? (a) Wichita, January average high 40 F and July average high 93 F (b) Wichita, January average high 40 F and July average high 72 F (c) Wichita, January average high 56 F and July average high 93 F (d) Wichita, January average high 56 F and July average high 72 F 28. Compared with most cities in the US, Tucson has a large daily temperature spread (difference between the high temperature and the low temperature). Which of the following is NOT a reason why Tucson has a large daily temperature spread? (a) Continental location (away from Oceans) (b) Relatively low latitude location (c) Relatively high altitude location (d) Generally clear skies (lack of cloud cover) Short Answer Section Select and answer 5 out of the 7 questions. Each answer is worth 7 points. Be concise. You should not need more than 2 or 3 sentences to answer each question. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. If you need more space, please use the back of the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Why did I define meaningful climate change to occur over small ecosystem-sized spatial scales instead of defining it as a change in global average temperature? Current climate models may be able to accurately predict changes in global average temperature, but cannot accurately predict ecosystem-scale climate changes. Why is this a problem for climate change impact studies? 2. How is the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere changing and why is it changing? What is the “missing sink” problem for atmospheric carbon dioxide. 3. Life on Earth can be said to be both fragile and robust with respect to climate changes that have occurred throughout the history of the planet, including climate changes that may be caused by human actions. Briefly explain. 4. In the documentary, “An Inconvenient Truth”, Al Gore uses the correlation between past temperature changes and carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere as inferred from ice core data (see graphs below) as evidence to make the prediction that because we have caused carbon dioxide levels to be 379 ppm today (off scale on the graph below), there is no doubt that global average temperature will rise to be off the chart as well. What is wrong with using this correlation as evidence for Al Gore’s prediction? 5. Shown below are two different reconstructions of past changes in global average temperature over the last 1000 years. The one on the left is known as the “hockey stick”, while the one on the right was part of an in-class handout. How can these two reconstructions look so different, and yet each is accepted as scientifically valid by many climate scientists? How might the differences between these two temperature reconstructions influence how someone views the present warming trend in global average temperature? 6. Recall the “shadow rule” with regard to ultraviolet exposure, which states “if your shadow is longer than your body, then you probably don’t need to apply sunscreen.” Your shadow is longer than your body when the solar angle is larger than 45. Using the plot of solar declination provided below, roughly estimate the time period over which sunscreen is not necessary at solar noon in Tucson (located at 32 North latitude) based on the shadow rule. Your answer should be a date range, such as June 10 – August 27 for example. Be sure to describe how you determined your answer. 7. Radiation from the sun contains photons of all visible colors of light. Explain why the disk of the sun looks red at sunrise by describing what happens to visible photons on their journey from the sun through space and through the atmosphere to your eyes.