* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8889298
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
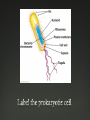
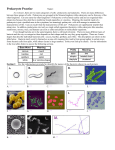
One main chromosome, circular in shape. Many satellite rings of DNA called plasmids. Prokaryotes do not have any membrane-bound organelles. All of these. None of these are found in eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria And Chloroplasts A small prokaryote with the ability to make its own food (chloroplasts) or use oxygen to efficiently metabolize food (mitochondria) was engulfed by a larger prokaryote and they lived happily ever after (symbiotically). Prokaryotic cells do not have added surface area in the form of membranebound organelles. Their surface area (cell membrane or supply of nutrients) grows by the square of length while their volume (metabolic demand) grows by the cube. They get DNA from other sources: Transformation (taking in naked DNA) Transduction (delivered by viruses) Conjugation (other bacteria thru sex pili) Generation time 20 min.(ideal) Haploid (no “hidden” traits) Share beneficial traits by conjugation. Decomposers: Recycle building blocks, Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, Biotechnology (plasmids + bio-factories) Rod-shaped: bacillus Spherical: coccus Spiral: spirilla E. coli, Anthrax, Whooping Cough, Pink Eye, Salmonella, Typhoid Fever, Pneumonia, Plague. Gonorrhea (pairs), Streptococcus (chains): Strep Throat, Scarlet Fever, Meningitis Staphylococcus aureus (clusters) Staph Infection: most common cause of skin infection, MRSA is serious. Lyme disease, cholera, syphilis Coccus (Streptococcus-chains) Spirilla (syphilis) Bacillus (E. coli) Coccus: Staphylococcus (clusters) antibiotics penicillin Fungi (molds) make natural antibiotics for their own defense against bacterial infection. Heterotrophic (grazers), anaerobic (fermenters), prokaryotes (bacteria). Photosynthesis/produced oxygen Endospores Bacteriorhodopsin Yes Their plasma membrane. The plasma membrane Into the cell where ATP is synthesized and used by the cell. Bacteriorhodopsin -Halobacteria (salt-loving) -Archaea bacteria -mechanism markedly different and simpler than chl.a. -photoactive enzyme -Each photon pumps one H+ out of cell -7 helices (green) with Retinal (blue) at center -Photon changes Retinal from cis- to trans-configuration -Moves the H+ across membrane and out of the cell Animation: Garland Science Transforming Light into Chemical Energy using Bacteriorhodopsin Cell Animation: bR, ATPsynthase, flagellum Owens Lake, CA Graph I Since BRP already occupied the green absorption niche, other pigments would have to evolve using available wavelengths for energy resulting in chlorophyll a’s absorption spectrum. End of Bacteria Review