* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sequencing by Synthesis
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
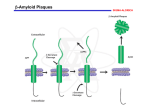
Article #3: A High-Coverage Genome Sequence from an Archaic Denisovan Individual Science 338:222(2012) Made Possible By: Improved Ancient DNA Recovery Method (from ssDNA) Improved DNA Sequencing Technology Denisova Cave in Siberia -source of bone fossils from Neandertal and Denisovan Archaic Human Groups Next Generation Sequencing Technology (Sequencing by Synthesis) Genetic Features Unique to Modern Humans -became fixed after divergence from Denisovans and Neandertals 111,812 Single Nucleotide Changes (SNCs) 9,499 insertions and deletions 260 SNCs result in amino acid change, 72 affect splicing patterns, 35 affect transcription Among 23 most conserved changes in modern human populations, eight affect brain function or nervous system function (cell adhesion, energy metabolism, microtubule assembly, neurotransmission) Some implicated in autism and other neurological disorders Article #4: Mitochondrial Alterations near Amyloid Plaques in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model Journal of Neuroscience 33:17042 (2013) What was known before the study? In vitro studies suggested a link between Amyloid β plaques and mitochondrial dysfunction. What new question is the study trying to answer? All evidence suggesting this link comes from in vitro or post mortem studies. An animal model is needed for in vivo studies. What reagents or techniques were needed for the study? APPswe:PSEN1dE9 transgenic mice-already made Multiphoton Microscopy Amyloid β Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease Aβ42 tau outside cells inside cells Mutations associated w/ familial early onset Alzheimer’s: APP and γ-secretase subunits (PSEN) APPswe:PSEN1dE9 human disease-associated alleles Multiphoton Microscopy Another super-resolution microscope with low phototoxicity Uses two laser beams of low energy, long λ infrared light to simultaneously excite a fluorochrome to emit higher energy, short λ light in fluorescent range -optical sectioning effect without pinhole aperture (at point of 2 laser beam dissection): improving resolution -low energy long λ light minimizes phototoxicity and allows penetration to greater depths in specimen (500 µm in this study) (lattice light sheet 100 µm) Fig. 1 Mitochondrial loss and structural abnormalities in living APP/PS1 transgenic mouse brain. A) mt-GFP observed in layer II-IV neuronal mitochondria (Lentiviral Infection) -no toxicity from mtGFP B) mtGFP staining absent w/in 16 μm zone of Methoxy X04labeled Aβ plaques C) AAV mediated expression of neuronal cytoplasmic GFP & mtGFP: similar absence of mtGFP near plaques D) dystrophic morphology of GFP-labeled neurites lacking intact mitochondria near plaques E) Decrease in COX IV immunostaining near plaques Fig. 2 Mitochondrial fragmentation in living APP/PS1 transgenic mouse brain. Tg wt Xie H et al. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:17042-17051 -mt-GFP in cable-like structures (2-30 µm long) of axons in wt mice -mtGFP in shorter fragmented cables (2-4 μm long) near plaques only in Tg mice Fig. 3 MMP was not altered in areas far from amyloid plaques in the APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Tests of MMP-sensitive (MTR and JC-1 aggregate) vs MMP-insensitive (MTG and JC-1 monomer) mitochondrial stains -FCCP treatment used to perturb MMP: both dyes can be used to monitor MMP by Multiphoton Microscopy No MMP defects observed in brain areas far from plaques Xie H et al. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:17042-17051 Fig. 4 Impairment of MMP near amyloid plaques in living APP/PS1 transgenic mouse. A) -reduction in both J-a and J-m near plaques (fewer mitochondria) -also reduction in J-a/J-m ratio near plaques (w/in 20 µm zone) B) Similar observation w/ TMRE (MMP-sensitive) C) Similar observation w/ MTR (MMP-sensitive) vs MTG (MMP-insensitive) D) Similar mitochondrial defects NOT observed near amyloid plaques in smooth muscle cells of leptomeningeal vessels in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Fig. 5 Reduced MMP in dystrophic neurites in living APP/PS1 transgenic mouse. TMRE staining was observed in GFP-labeled neurites (even in dystrophic ones near plaques) but intensity reduced in those near plaques Fig. 6 Oxidative stress accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction in living APP/PS1 mouse. -used redox-sensitive GFP variants to assess oxidative stress near plaques roGFP: excites at 900nm when reduced and at 800 when oxidized Oxidative stress roGFPex800 observed in dystrophic neurites and neurons near plaques and contain mitochondria with reduced MMP (TMRE) Xie H et al. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:17042-17051 What did we learn from the study? The majority of mitochondria in brains of mice with amyloid plaques are NORMAL. Defects in mitochondrial density, composition, MMP, redox and ROS status only observed in zone surrounding plaques. What remaining/new questions need to be addressed? (Differs from in vitro work where amyloid plaque burden artificially high) Establish a timeline for Amyloid β accumulation, mitochondrial abnormalities, oxidative stress, and altered intracellular Ca2+ levels (cause/effect relationship) Are there any caveats to the conclusions? Potential for therapies aimed at mitochondrial function (See article on Sirtuins in treatment of Parkinsons Disease) Cause vs. Effect?