* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 16
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
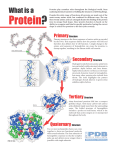
Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics GCBA815, Fall 2015 Week-16: Structural Bioinformatics Babu Guda Department of Genetics, Cell Biology and Anatomy University of Nebraska Medical Center __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Structural Bioinformatics __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 1 Structural View of Biology • The function of a biological macromolecule is highly dependent on its structural confirmation • Deciphering the structure of DNA (double-helix) has revolutionized molecular biology research • Similarly, understanding the structure of proteins/enzymes help researchers to identify suitable drug targets and design appropriate drugs • While a lot of proteins act as enzymes, there are a number of structural proteins that support cellular and tissue-level infrastructure and aid in intra and inter cellular communication __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Binding of a drug compound to a cancer-related protein, MDM2 Human cancer-related protein (MDM2) with embedded small-molecule drug compounds (“nutlin”). MDM2 is shown as stick figures; “nutlin” is shown as small cyan colored spheres (van der Wall’s radii). Picture taken from BayeNetwork __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 2 Nutlin-MDM2 binding activates P53 • Nutlins are cis-imidazoline analogs that can inhibit the interaction between MDM2 and tumor suppressor P53, a tumor suppressor gene • It stabilizes P53, which induces senescence (growthinhibition) in cancer cells. • Nutlin family of small molecules are widely used in anticancer studies • The structure of MDM2 bound to Nutlin was solved (4HG7) to understand how Nutlin binds to MDM2. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Structural protein examples • Actin: Support the size, shape, structure and motion of cells • Cadherin: Adhesive proteins that glue cells together • Clathrin: Vesicular trafficking • Collagen: About 25% of all protein in our body • Integrins: On the cell surface, linking cells • Vaults: Symmetrical shells made of vault proteins • PDB-101: • http://pdb101.rcsb.org/ • http://mm.rcsb.org/ • http://pdb101.rcsb.org/learn/resources/videos __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 3 The 20 natural amino acids __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Structural Forms of Proteins Primary structure: The linear amino acid sequence of the polypeptide (PP) chain including post-translational modifications and disulfide bonds. n Secondary structure: Local structure of linear segments of the PP backbone atoms without regard to the conformation of the side chains. n Tertiary structure: The three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a single PP chain. n Quaternary structure: The arrangement of separate PP chains (subunits) into the functional protein n Bovine Mitochondrial F1-Atpase (ATP Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Synthase Chain Heart Isoform; Ec: Protein Kinase 3.6.1.34) Chain α : A, B, C; Chain β: D, E, __________________________________________________________________________________________________ F; Chain γ: G Fall 2015 GCBA 815 4 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Protein Data Bank (PDB) http://www.rcsb.org/pdb __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 5 Rodes, 2006 6 7 Protein structure data format: PDB __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 PDB IDs • Four letter code for the compound, case insensitive (Ex: 2HHB) • Always start with a numeric followed by alphanumeric • Each compound may have multiple chains, a chain ID is denoted by compound ID followed by ‘:’ and chain identifier (Ex: 2HHB:A) • If the compound has only one chain (monomer), ‘_’ denotes the chain position (Ex: 1BBS:_) 8 Structure Alignments • Structural alignment involves establishing equivalencies between residues in two or more proteins based on their 3D-coordinates • 3-D coordinates from C-α atoms are most commonly used for calculation of distance in structural alignments L L F I R K R K F F G R L W G P __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 Protein 3-D Visualization Tools • Jmol (http://jmol.sourceforge.net) • Simple viewer (PDB) • Protein workshop (PDB) • QuickPDB viewer (PDB) • DeepView - Swiss-Pdb Viewer (http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/) • PyMOL (http://ww.pymol.org) • KiNG viewer (http://http://kinemage.biochem.duke.edu/software/king.php) 9 Visualization of Protein Structures • All Alpha: • Haemoglobin – 1BAB • K+ Channel Protein - 1BL8 • All Beta : Porin - 2POR • Mixed Alpha-beta: TIM barrel -1YPI Beautiful Protein Structures • Hemolysin (7AHL) • Ribonuclease inhibitor (2BNH) • Hydroperoxide resistance protein (1VLA) 7AHL 2BNH 1VLA __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fall 2015 GCBA 815 10