* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TNS03%20Introduction%20to%20Network%20Security
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
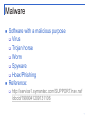
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Security Essentials wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to Network Security Source: Chapter 1 Computer Security Fundamentals Chuck Easttom, Prentice Hall, 2006 Modified by: C F Yung Objectives Identify top threats to a computer network Assess the likelihood of an attack Define key terms like cracker, sneaker, firewall, and authentication (證明) Compare and contrast perimeter and layered approaches to network security Use online resources 2 Introduction Computer systems and networks are all around us Online banking Automated supermarket checkouts Online classes Online shopping Online travel resources 3 Introduction (cont.) How is personal information safeguarded (維 護)? What are the vulnerabilities (弱點)? What secures these systems? 4 How Seriously Should You Take Threats to Network Security? Which group do you belong to? “No one is coming after my computer.” “The sky is falling!” Assumes there is no real threat (威脅) Reactive approach to security Overestimate the dangers Middle ground 5 Identifying Types of Threats Malware – MALicious (懷惡意的) softWARE Intrusions DoS – Denial of Service attacks 6 Malware Software with a malicious purpose Virus Trojan horse Worm Spyware Hoax/Phishing Reference: http://service1.symantec.com/SUPPORT/nav.nsf /docid/1999041209131106 7 Malware (cont.) Virus A small program that replicates (複製) and hides itself inside other programs, usually without the knowledge of the user. Two criteria: Usually spreads through e-mail Must execute itself Must replicate itself Using victim’s email account to spread the virus to everyone in their address book. Uses system resources, causing slowdown or stoppage. Heavy network traffic caused by the virus replication. 8 Malware (cont.) Trojan Horse The other most common kind of malware. Named after the wooden horse of ancient history. Appears to be benign (良好) software but secretly downloading a virus or other malware. For a Trojan horse to spread, you must invite these programs onto your computers. For example, by opening an email attachment or downloading and running a file from the Internet. 9 Malware (cont.) Trojan Horse Some may cause immediate damage, others might be designed to provide remote access to the system via a “back door”. Some may sit and wait to perform actions as instructed remotely, such as collecting and sending keystrokes captured by a keylogger program running in the background. 10 Malware (cont.) Worm Worms are programs that replicate themselves from system to system without the use of a host file. This is in contrast to viruses, which requires the spreading of an infected host file. Use e-mail and network facilities to spread to other resources. 11 Malware (cont.) Spyware Software that literally spies on what you do on your computer. The most rapidly growing type of malware Cookies Key logger Unlike viruses and worms, spyware does not usually selfreplicate. Exploits infected computers for commercial gain. Typical tactics include delivery of unsolicited (未經請求) popup advertisements, theft of personal information (including financial information such as credit card numbers) Monitoring of Web-browsing activity for marketing purposes, and routing of HTTP requests to advertising sites. 12 Malware (cont.) Hoax (惡作劇) Do not contain any code, instead relying on the gullibility of the users to spread. Often use emotional subjects such as a child's last wish. Any e-mail message that asks you to forward copies to everyone you know is almost certainly a hoax. Phishing Phishing scams are targeted to gather personal information in order to hijack your assets or steal your identity to open credit accounts in your name. Sample: http://news.alibaba.com/article/detail/safetrading/100068729-1-fraud-email-samples.html http://www.wikihow.com/Spot-an-Email-Hoax-or-PhishingScam 13 Compromising System Security 損害系統安全 Intrusions Attacks attempt to gain unauthorized access to your system resources. Hackers Crackers Social engineering War-driving (wireless networks) Ref: http://www.pisa.org.hk/ 14 Denial of Service Attacks (DoS) The attacker does not intrude into the system, just blocks access by authorized users. To flood the targeted system with so many false connection requests that the system cannot respond to legitimate requests. Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denial-ofservice_attack 15 Common Attacks on Your Network Viruses Catch up on new and refurbished viruses http://www.hkcert.org Unauthorized use of systems DoS attacks Intrusions Employee misuse Insider attacks http://www.securityfocus.com/infocus/1546 16 Basic Security Terminology People Hackers (Experts on a particular system) White hats Black hats (Crackers) Conduct illegal activities for reasons they feel are ethical, such as hacking into a system belonging to a corporation that the hacker feels is engaged in unethical activities. Script kiddies Once gain access to a system, their goal is to cause some type of harm. Gray hats Upon finding a vulnerability in a system, will report the vulnerability to the vendor of the system. Download utilities and scripts to perform some hacking tasks. Ethical hackers (Sneakers) Employed to legally breaks into a system in order to assess security deficiencies. 17 Basic Security Terminology (cont.) Devices Firewall Proxy server Filters network traffic Hides IP address of internal host Improve performance and filter requests Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Monitors traffic, looking for attempted attacks (e.g. scanning all ports of a system) http://www.sans.org/reading_room/whitepapers/detectio n/337.php 18 Basic Security Terminology (cont.) Activities Phreaking (盜用電話線路) Authentication Involves breaking into telephone systems, say to make free long distance calls. Determine if the credentials (username, password) are authorized to access the resource. Auditing (審核) Reviewing logs and records Procedures to determine if these items meet standards 19 Network Security Paradigms 網路安全範例 How will we protect our network? Perimeter security approach Layered security approach Any technology or procedure to prevent unauthorized access of the network. Little or no effort is put into securing the systems within the network. Adequate for small organizations. Firewalls, proxy servers, password policies. Not only is perimeter secured, but individual systems within the network are also secured. Divide the network into segments and secure each segment. Proactive versus reactive Hybrid security method 20 Online Security Resources CERT (Computer Emergency Response Team) The first computer incident-response team. www.cert.org Microsoft Security Advisor A portal to all Microsoft security information, tools, and updates. www.microsoft.com/security/default.mspx F-Secure A repository for detailed information on viruses, tools for cleaning infected system. www.f-secure.com/security_center/security_alerts.html SANS A repository of security-related documentation. www.sans.org (ISC)2 A not-for-profit leader in educating and certifying information security professionals www.isc2.org 21 Analysis Tools Nmap (Network Mapper) Snort Open source network intrusion prevention and detection system. www.snort.org Nessus Free security scanner www.insecure.org/nmap/index.html Network vulnerability scanner www.nessus.org Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) Free security and vulnerability assessment scan tool. 22 Analysis Tools (cont.) Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) Free security and vulnerability assessment scan tool. Knoppix STD A Live CD Linux distribution based on Knoppix that focuses on computer security tools. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knoppix_STD 23 Summary Network security is a constantly changing field. You will require three levels of knowledge. First, take the courses necessary to train yourself in the basic techniques. Second, learn your enterprise system intimately, with all its strengths and vulnerabilities. Finally, keep current in the ever-changing world of threats and exploits. 24