* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download At its greatest extent it covered modern day…
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Sumptuary law wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
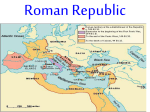
Rome AD 192 Where: At its greatest extent it covered modern day… France Spain Portugal Germany much of Britain North Africa and southwestern Asia Here is a comparison from your book of early Rome and later Rome c. 265 BCE (dark purple) and 117 CE (light purple) ROME When: Roughly, Mid 700’s BCE (to 476 CE) Who: Three Groups of people: Latins – settled near the middle of the peninsula Greeks – to the south Etruscans – to the north (the Etruscans gave Romans the arch) ROME What happened: • Etruscan kings take power in 600’s • By 509 Roman people remove their last king, a tyrant named Tarquin the Proud • It is at this time Rome became a republic (our type of government) • So, the period of Roman Republic and Empire is roughly 500 BCE to 500 CE ROME What is a republic? Citizens can vote for elected representatives These representatives make laws and run the republic They do this in a place called the senate (just like in our US government) ROME People of Rome Basically three classes of people: 1) Patricians 2) Plebeians 3) Slaves ROME Patricians: Upper Class Landowners Inherited Power Made the decisions Allowed to run for and hold office ROME Plebeians: Working Class Usually artisans, farmers , merchants, etc. Had some power (the right to vote) At first were not allowed to run for office Far outnumbered the patricians Question Given a choice between our Patricians and Plebeians who do you think holds the most power? If you guessed Patricians You are right! Basic Government Set Up Around 509 B.C Consul (2) Senate (300) ROME Who runs the Senate? Two representatives called Consuls Consuls work together (like co-presidents maybe?) for a term of one year One consul runs the government and people The other would take charge of the military Both were elected and therefore answered to the senate You will serve but not represent! I don’t know we just go where the consuls tell us. Why are we fighting again? So not fair, we should have a say in things! Conflict of Orders (conflict between the two classes) 494 B.C.- Plebeians marched out of city Why would that be an issue? What came of it Tribunes- 2 (grew to 10) spoke for plebeians in Senate. Veto- right to override a decision. Council of Plebs- could make laws in regards to Plebs only. Still had little power and laws were not written down? Do laws need to be written down? ROME The Twelve Tables: 451 BCE Another step towards equality Tribunes write down laws Laws carved on twelve tablets that become known as the Twelve Tables ROME Twelve Tables become basis for later Roman Law Establish the idea that all citizens have rights to protection under law. Now the laws are written Plebeians continue to gain rights 367 B.C. – One of the two councils had to be plebeian. 287B.C.- Plebeians can pass laws for all citizens. Eventually could be elected into Senate Basic Government Set Up 200 years or so later (from 509 setup) Consuls(2) Senators (300) Tribunes(10) ROME This system of government lasted for almost five hundred years But by 60 BCE trouble was brewin’….