* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Foundations of Rome
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Sumptuary law wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
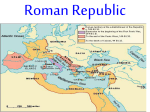
SECTION ONE Geography Italy’s physical features aided the growth of a powerful civilization To the north, the peninsula was protected by the high mountains of the ALPS - Sea provided both protection and a means of rapid transportation - Rich soil and a mild climate, able to support a large population. - Rome founded on the Tiber River– great for trade. - Etruscans At first, Rome was ruled by Latin kings. Around 616 BC, Rome came under the rule of the Etruscans of northern Italy. Great metalworkers and jewelers whose culture had been heavily influenced by Greece. - Built Rome’s first city walls and sewer Introduced building techniques (the Arch) Introduced alphabet and number system Introduced gladiator games and chariot races Influenced style of sculpture and painting. ROME BECOMES A REPUBLIC The Etruscans rule ended in 509 BC when the last king, a tyrant, was thrown out. In place of the monarchy, a Republic was established. Republic- elected officials govern the state Patricians In the early days, the heads of a few aristocratic families, known as PATRICIANS, who were elected officials from among themselves, ruled. Controlled every aspect of society – politics, religion, economics, and the military. They maintained their power through a patronage system in which wealthy Romans provided financial, social, or legal support for lower ranking families in return for their support. Plebeians Common People = PLEBEIANS Challenged the power of the patricians. Invaders (wouldn’t fight) Patricians needed them- had to expand their rights. To guarantee their rights, the plebeians also gained the right to elect officials known as TRIBUNES. -- It was the tribunes’ job to protect the plebeians against unjust treatment by patrician officials. ** Tribunes even gained the right to VETO, or ban laws that seemed harmful or unjust to the plebeians. What is this cartoon describing? ROMAN FORUM Forum- central square Plebeians forced the patricians to write down all the laws. These laws would be displayed in the Roman Forum on 12 large bronze tablets. As a result, the code became known as the Law of the Twelve Tables. ^^ This way, judges could not make decisions based on opinions or secret laws. Republican Government 1. 2. 3. Together the two groups created a practical and flexible unwritten Constitution, or a political structure. The Romans also created new offices and institutions of government. SENATE: a body of 300 members who advised elected officials, controlled public finances, and handled all foreign relations. Various popular assemblies, in which all citizens voted on laws and elected officials Officials called Magistrates, put laws into practice, governed in the name of the Senate and the people and acted as priest. Government The last king of Rome was taken over by CONSUL- chief executives and commanders of the army. -`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`-`CHECKS & BALANCES Magistrates presided over Elected Magistrates the Senate Tribunes could veto officials’ actions Senate could refuse to give magistrates money. Assemblies could reject laws approved by the Senate Assemblies & Tribunes Senate