* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Office hours
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
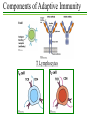
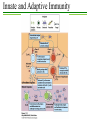
Intro-BIOL318 Immunology Instructor: Dr. Kathy Szick-Miranda Office: Science I 316 Phone: 654-6165 Email: [email protected] Web: www.csub.edu/~kszick_miranda Office hours: M 10-12; T 3:30-5; W 10-11:30 Lecture and Discussion: T R 10:00-11:40am, Sci II 180 Intro-BIOL318 Immunology Course Objectives: Upon completion of this course students will be expected to: •Describe the various cells and organs of the immune system, including the role of each during the immune response. •Compare and contrast innate and acquired immunity, including their specific components and effector mechanisms. •Describe antigens and antibodies and their interactions. •Discuss the immune response to specific pathogens. Intro-BIOL318 Immunology Assignment Point Values: Exam I Exam II Final Exam (Exam III) Quizzes (top 5 scores) TOTAL 100pts 100pts 100pts 50pts 350pts Historical Perspective Immunity - state of protection from an infectious disease. 430 BC – Greek historian Thucydides - Athenian plague 15th century – Chinese attempts to induce immunity 1718 – Mary Wortley Montagu – innoculated her children 1798 – Edward Jenner – milkmaids and cowpox/smallpox Historical Perspective Louis Pasteur early 1880’s – Cholera and chickens Attenuation hypothesis 1881 – Testing the hypothesis with anthrax and sheep 1885 – Rabies vaccine Historical Perspective 1890 - Behring and Kitasato – link serum to immunity 1883 – Metchnikoff – links cells (phagocytes) to immunity early 1900’s – many functions of immune serum 1930’s – Kabat - immunoglobulin/antibodies 1950’s – Glick – two types of lymphocytes Historical Perspective 1900 – Paul Ehrlich – Selective theory 1950’s – Jerne, Talmadge and Burnet – clonal selection theory Historical Perspective Infection and Immunity pathogens – organisms causing disease pathogenesis – the means by which disease-causing organisms attach a host. Innate and Adaptive Immunity Innate Adaptive 1st line of defense 2nd line of defense Non-specific mechanisms Highly specific mechanisms Phagocytes and recognition molecules Lymphocytes, antigen specific receptors, antibodies Components of Adaptive Immunity T Lymphocytes Innate and Adaptive Immunity Innate and Adaptive Immunity Immune Dysfunction Allergies and asthma Graft rejection Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency