* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IMMUNE SYSTEM SPECIFIC DEFENSE
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
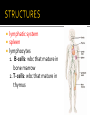
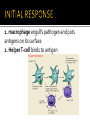
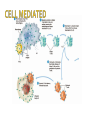
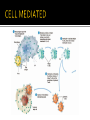
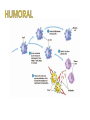
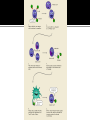
PP. 961-966 lymphatic system spleen lymphocytes 1. B-cells: wbc that mature in bone marrow 2. T-cells: wbc that mature in thymus There are many different lymphocytes (wbc) Each have receptors for different antigens (markers) Antigen: Identifies cell as foreign 2-part attack Cell-mediated: Killer T-Cell production Humoral: B-Cell production Starts with an initial response Initial response Cell-mediated T-Cell production Humoral B-Cell production 1. macrophage engulfs pathogen and puts antigens on its surface 2. Helper T-cell binds to antigen 3. Macrophage releases a chemical (INK-1) which causes the Helper T-cell to release INK-2 INK-2 Cell-mediated T-Cell production Initial response INK-2 Humoral B-Cell production INK 2 stimulates the production of more Helper T Cells and Cytotoxic T Cells Cytotoxic T Cell (killer T cell): kills infected body cells. Initial response Cell-mediated T-Cell production Humoral B-Cell production INK-2 causes complimentary B-cells to divide Most B-cells change to plasma cells Plasma cells produce antibodies Y-shaped protein that deactivates pathogen and clumps them making it easier for macrophages to engulf and destroy them. Some B-cells become memory cells and store information about pathogen Body’s long term defense system When exposed to pathogen a 2nd time, memory cells immediately recognize and destroy it before it causes illness. primary: 1st time body encounters pathogens secondary: 2nd time body encounters pathogen with memory cells (leftover B-cells and T-cells) Immunity: ability to resist an infectious disease Vaccination: introduction of antigens into body to cause immunity Vaccine: solution of dead or weakened pathogens that contains pathogens Antigens produce a primary immune response Memory cells created provide quick secondary immune response if antigen enters body again. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation__the_immune_response.html Some Diseases that have been controlled through vaccines: polio, measles, mumps, tetanus, and small pox