* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IMMUNE SYSTEM NON-SPECIFIC DEFENSE
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
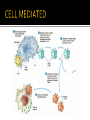
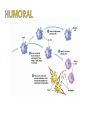
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup