* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Red blood cells - Maria Regina School
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
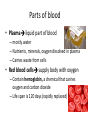
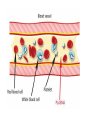
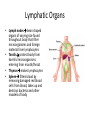
Blood and Lymphatic System Functions of Blood • Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells • Carries carbon dioxide from body cells to lungs • Carries waste products from cells to kidneys • Transport nutrients to cells • Fights infections and heal wounds Parts of blood • Plasma liquid part of blood – mostly water – Nutrients, minerals, oxygen dissolved in plasma – Carries waste from cells • Red blood cells supply body with oxygen – Contain hemoglobin, a chemical that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide – Life span is 120 days (rapidly replaced) Parts of Blood • White blood cells fight bacteria and viruses – Body reacts to invaders by increasing WBC – WBC enter infected tissue, destroy bacterial/viral invaders, absorb dead cells – Life span a few days to many months • Platelets irregularly shaped cell fragments that help clot blood – Release chemicals that form filaments of fibrin – Life span 5-9 days Blood Clotting • Platelets and clotting factors plug up wound – Platelets stick to wound and release chemicals – Clotting factors carry out chemical reactions – Threadlike fibers called fibrin form sticky net • Net traps blood cells and plasma, forming clot – Skin cells begin repair process Blood Types • A, B, AB, O • Based on antigens – Chemical ID tags on blood – Type O has no antigens so can donate to everyone • Based on antibodies – Proteins identify substances that don’t belong in body and destroy them – AB has no antibodies so can receive from anyone • Based on Rh factor – People who lack Rh factor (negative type), – Have Rh factor are positive (like being O+) – If lack Rh but receive Rh positive blood, body will produce antibodies against blood which can cause blood clots. Blood Disease • Anemia affects red blood cells – Body tissues don’t get enough oxygen and are unable to carry on usual activities – Causes include loss of large amount of blood, diet lacking iron, or heredity • Leukemia affects white blood cells – WBC made in excessive numbers, but are immature and don’t fight infection well – Immature cells fill up bone marrow and crowd out normal cells Lymphatic System • Collects tissue fluid and returns it to blood • Lymph tissue fluid that has diffused into lymphatic capillaries – Contains water and dissolved substances – Contains lymphocytes, a type of WBC that helps body defend itself – Carried through lymphatic capillaries and vessels to large veins near heart – Moved by muscle contractions – Has valves to keep lymph from flowing backward Lymphatic Organs • Lymph nodes bean shaped organs of varying size found throughout body that filter microorganisms and foreign material from lymphocytes • Tonsils protect body from harmful microorganisms entering from mouth/throat • Thymus makes lymphocytes • Spleen filters blood by removing damaged red blood cells from blood, takes up and destroys bacteria and other invaders of body Lymphocytes • The HIV virus attacks lymphocytes called helper T-cells