* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
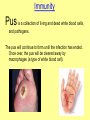
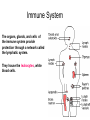
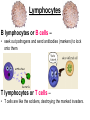
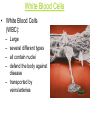
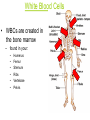
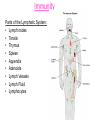
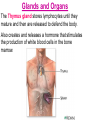
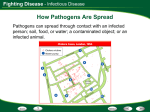
Immune System Immune System Pathogens are disease-producing agents, such as bacteria and viruses. CUTS AND PUNCTURES How do pathogens get into the body? Openings EYE NOSE MOUTH Immune System Disease can be transmitted to humans in various ways: Insects Common inanimate objects Airborne droplets or dust particles Immune System And of course… Touch Immune System What causes disease? Treatment for disease? • Viruses • Vaccines • Bacteria • Antibiotics Immunity Skin is your first line of defense. Body secretions (mucus, oil, sweat, tears, and saliva) provide protection from pathogens. Immunity • If a pathogen gets passed your skin, the next step is inflammation of the tissues. – Redness, Swelling, Pain, and Heat are all part of the immune response to rid your body of harmful agents. – White blood cells rush to the scene of the accident to prevent the spread of the pathogen. You can own your own Red Blood Cell & White Blood Cell…. Call now! Supplies are limited! Immunity Pus is a collection of living and dead white blood cells, and pathogens. The pus will continue to form until the infection has ended. Once over, the pus will be cleared away by macrophages (a type of white blood cell). Immune System The organs, glands, and cells of the immune system provide protection through a network called the lymphatic system. They house the leukocytes, white blood cells. Types of Leukocytes: • Phagocytes: cells that engulf (take in), destroy, and digest invading organisms. • Lymphocytes are cells that allow the body to remember and recognize previous invaders. When pathogens invade, leukocytes begin defending right away Lymphocytes B lymphocytes or B cells – • seek out pathogens and send antibodies (markers) to lock onto them T lymphocytes or T cells – • T cells are like the soldiers, destroying the marked invaders. White Blood Cells • White Blood Cells (WBC): – – – – Large several different types all contain nuclei defend the body against disease – transported by veins/arteries White Blood Cells • WBCs are created in the bone marrow – found in your: • • • • • • Humerus Femur Sternum Ribs Vertebrae Pelvis White Blood Cells Think of bone marrow as the cream filling of a Twinkie! Immunity Parts of the Lymphatic System: • Lymph nodes • Tonsils • Thymus • Spleen • Appendix • Adenoids • Lymph Vessels • Lymph Fluid • Lymphocytes Glands and Organs Lymph nodes: small masses of tissue that store lymphocytes and filter pathogens from the body. Where are they found in your body??? Lymph nodes swell when you have a viral or bacterial infection Glands and Organs The spleen stores some lymphocytes, and filters and destroys bacteria and worn out red blood cells….in other words it cleans the blood. Glands and Organs The Thymus gland stores lymphocytes until they mature and then are released to defend the body. Also creates and releases a hormone that stimulates the production of white blood cells in the bone marrow. Immune System QUIZ 1. What is a pathogen? 2. How do pathogens enter the body? 3. What type of cell engulfs pathogens? 4. What system is responsible for immunity? 5. What is the difference between a B cell & a T cell?