* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
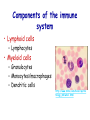
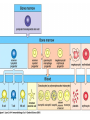
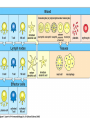
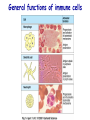
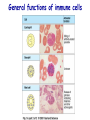
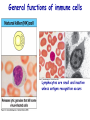
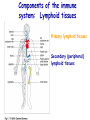
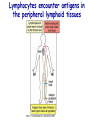
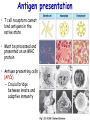
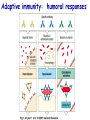
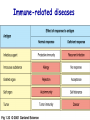
Introduction to immunology Jan. 19 Reading: Chapter 1 Objectives • Compare and contrast the general functions of different types of immune cells • Summarize the roles of: – innate versus adapative immunity – cellular versus humoral immunity History of immunology • Early observers noticed that survivors of certain diseases were resistant to re-infection Mary Wortley Montagu Excerpt from a letter by M. W. Montagu, 1717: “….The old woman comes with a nutshell full of the matter of the best sort of smallpox and asks what veins you please to have opened. She… puts into the vein as much venom as can lie upon the head of her needle. …You may believe I am very well satisfied of the safety of the experiment since I intend to try it on my dear little son. …I should not fail to write to some of our doctors very particularly about it if I knew any one of 'em that I thought had virtue enough to destroy such a considerable branch of their revenue for the good of mankind….” http://www.foundersofscience.net/lady_mary_montagu.htm History of immunology • • Edward Jenner, 1796 – 1st vaccinations: cowpox (vaccinia) Louis Pasteur, 1880s – Vaccines against cholera in chickens, rabies • Emil von Behring & Shibasaburo Kitasato, 1890 – Serum from animals immune to diptheria or tetanus conferred immunity to recipients – “Antitoxic activity” = antibodies History of immunology • Eli Metchnikoff (shared Nobel Prize, 1908) – • Phagocytic cells Paul Erlich (shared Nobel Prize, 1908) – Described different types of immune cells, antibodies Components of the immune system • Lymphoid cells – Lymphocytes • Myeloid cells – Granulocytes – Monocytes/macrophages – Dendritic cells http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/his tology_mh/wbc1.html Hematopoiesis General functions of immune cells General functions of immune cells General functions of immune cells Lymphocytes are small and inactive unless antigen recognition occurs Components of the immune system: Lymphoid tissues Primary lymphoid tissues Secondary (peripheral) lymphoid tissues Inflammation is triggered by infection Lymphocytes encounter antigens in the peripheral lymphoid tissues Two general types of immunity • Innate (natural, native) • Adaptive (specific, acquired) Innate vs adaptive immunity Innate immunity Response time Number of specificities Specificity improves during response Memory responses Adaptive immunity Innate immunity • Phagocytes (macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells) – Engulf microbes or foreign particles – Release proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines • Complement • Inflammation (early) • Antigen processing and presentation Antigen presentation • T cell receptors cannot bind antigens in the native state • Must be processed and presented on an MHC protein • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Crucial bridge between innate and adaptive immunity Adaptive immunity • APCs required • Lymphocytes activated • Effector mechanisms respond to different types of pathogens – Humoral (B cells, antibodies) – Cell-mediated (T cells) • Memory cells generated Adaptive immunity • Lymphocyte activation – Clonal selection and clonal expansion Adaptive immunity: humoral responses Adaptive immunity: cell-mediated immunity • Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+, CTL) – Recognize antigens presented by MHC I – Response to cytosolic pathogens – Directly lyse target cells Adaptive immunity: cell-mediated immunity • Helper T cells (CD4+) – Recognize antigens presented by MHC II – Response to extracellular pathogens – 3 major classes: • TH1 • TH2 • Regulatory T cells – Boost proliferation and function of other immune cells Immune-related diseases