* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Innate Immunity - University of California, Los Angeles
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
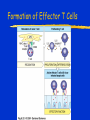
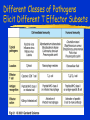
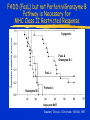
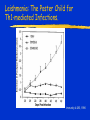
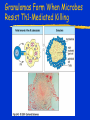
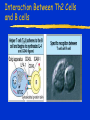
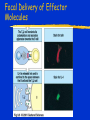
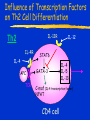
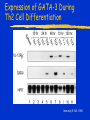
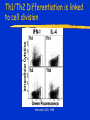
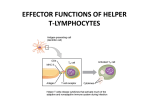
Immune Effectors Kathleen Kelly [email protected] 6-5562 Reading Immunobiology (5th Edition) Janeway, Travers, Walpert and Capra Chapter 10 (p. 381-402) and Chapter 8 (p. 295-340) Agnello D, et al. Cytokines and transcription factors that regulate T helper cell differentiation: new players and new insights. J Clin Immunol. 23:147-161, 2003. Mak, TM & Lohoff. Roles of Interferon Regulatory Factors in T-helpercell Differentiation. Nature Reviews Immunol. 5:125-135, 2005. Russell, JH & Ley, TJ. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 323-370, 2002. Formation of Effector T Cells T Effector Cells T cell subsets are the armed assassins of the adaptive immune response CD8 Cytotoxic T cells (CTL) Effector function is to lyse target cells (infected, tumor) CTL - effector molecules are lytic granules perforin/granzyme pathway CD4 T helper cells Effector function is to produce certain cytokines Th1 - effector cytokine is IFNg • - Activate MQ & FasL/FADD mediated cytotoxicity Th2 - effector cytokine is IL-4 • - help B cells/Ab production Different Classes of Pathogens Elicit Different T Effector Subsets Effector Function of CTL Effector function is to lyse target cells Virus infected Tumor MHC Class I restricted Contact-dependent Perforin/Granzyme mediated cytotoxicity Lytic granules are produced & released from CD8+ CTL Granules induce apoptosis Pathways of Apoptosis Cytotoxic granules Russell, JH Ann. Rev. Immunol. 20:323, 2002 Granzyme B but not FADD (FasL) Pathway is Necessary for MHC Class I Restricted Responses (GvH) Syngeneic FasL & Granzyme B-/Wild Type FasL-/- Granzyme B-/- Graubert, TA et al. J Clin Invest. 100:904, 1997 FADD (FasL) but not Perforin/Granzyme B Pathway is Necessary for MHC Class II Restricted Response Syngeneic FasL & Granzyme B-/- FasL-/- Granzyme B-/- Perforin-/- Graubert, TA et al. J Clin Invest. 100:904, 1997 CTL Lytic Granules Lytic granules: Are synthesized de novo after initial T cell activation (1-3 days) (NK cell killing is immediate) After activation CTL can kill multiple cells, ie multiple times. Requires post-translational modification Perforin (action is Ca++ dependent) Similar in structure to C9, which polymerizes to form membrane pores on target cell surface by binding to perforin receptors that are induced by IFNg Granule Exocytosis Pathway Effector molecules are preformed in granules and undergo granule exocytosis pathway PI-3 kinase RAC-1 PAC-1 MAPK kinase ERK cation-dependent Mannose-P-6 R Russell, JH, Ann. Rev. Immunol. 20:323, 2002 CTL Lytic Granules Lytic granules: Granzymes Serine proteases • Granzyme B cleaves caspase 3 Other enzymes with undefined function Granulysin Orphan granzymes Action of Granzyme B Russell, JH Ann. Rev. Immunol. 20:323, 2002 Focal Delivery of Effector Molecules TCR : MHC-peptide complexes induces reorientation of cytoskeleton to contact site Microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) and golgi apparatus then follows Enhanced binding of LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) to ICAM-1(CD54) forms a molecular seal. Effector molecules are delivered within the sealed area CD8 Perforin/Granzyme is Needed to Clear CMV Infected Cells Mice infected with MCMV Eur. J. Immunol. 30:1350, 2000 Day 15 Day 30 Effector Function of Th1 Cells Th1 cells activate macrophages to induce intracellular killing of organisms that grow in vesicles MHC class II restricted response Endosomal processing pathway Th1 cells produce membrane-associated proteins soluble cytokines Effector Molecules of Th1 Cells Membrane bound CD40 ligand - sensitizes macrophages to respond to IFNg Fas ligand - induces apoptosis of target cell Soluble IFNg - activates macrophages & MHC class I & II and co-stimulatory molecules TNFa - activates macrophages & induces NO production GM-CSF - activates macrophages LT, TNF-b - activates macrophages & induces NO production Th1 Cytokines Leishmania: The Poster Child for Th1-mediated Infections. Immunity 4:283, 1996 Production of Th1 Effector Molecules Effector molecules must be synthesized – for each killing event 1-2 hrs after TCR stimulation. TCR receptor triggering induces Expression of CD40L Cytokines are made de novo This process minimizes “by-stander” activation BUT FasL receptor killing is more promiscuous that CTL granule release because it can occur in the absence of TCR stimulation. IFNg mRNA contains (AUUUA)n sequence in untranslated 3’ region that reduces the 1/2 life of mRNA Function of Other Th1 Effector Molecules Granulomas Form When Microbes Resist Th1-Mediated Killing Effector Function of Th2 Cells Help B cells produce antibody Linked recognition - T & B cells must “see” the same antigen but not identical epitopes MHC - class II antigen presentation activates Th2 cell to express CD40L CD40L - drives B cells into cell cycle IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13 - drives B cell proliferation (IL-6) & differentiation Isotype switching Th2 Cytokines Interaction Between Th2 Cells and B cells Focal Delivery of Effector Molecules CD4 T Cell Differentiation Process that occurs following the activation of naïve CD4 cells which directs Th1 or Th2 cell development Influenced by: Cytokines Th1: IL-12 & IFNg Th2: IL-4 Co-stimulatory molecules on APC Nature of the peptide:MHC ligand (dose, affinity) CD4 T Cell Differentiation Different patterns of cytokines were produced by T cell clones R. Coffman & T. Mosmann (1986) JI 136:2348 Listeria infection of macrophages induced IL12 production which was necessary for Th1 cell development K. Murphy (1993) Science 260:547-549 Lysteria monocytogenes: A model for inducing Th1 Differentiation Hsieh, C-S Science 260:547, 1993 Influence of Cytokines on T Helper Cell Differentiation IL-4 IL-12, IL-23, IL27 & type I IFNs Th1 IL-2 ThP ThIL-17 DTH & MQ activation Inflammatory pathology IL-17 IL-6 TNFa IL-12 Th2 IL-4, MCP-1? IFNg IL-2 LT (TNFb) IL-4 IL-5 Allergic reactions IL-10 & Eosinophilic IL-13 inflammation Th0 progresses to Th1 or Th2 PNAS 29:7565, 1995 Cytokines signal via JAK/STAT Pathway Jak2 Jak1 Tyk2 Jak3 ↑IL-12 ↑IL-4 Cytokine Receptor Families Influence of Transcription Factors on T cell subset Differentiation Th1 IL-12 TCR APC IL-12Rb (p40 chain) IFNg IL-18 2)STAT4 IFNgR IL-18R IL-23 p19 chain IL-12p40 1) STAT1 T-BET CXCL13 CXCR5 CCL9, 10 & 11 CXCR3 IFNg Th17 PSGL-1 Receptor IL-17 CD4 cell What are the progenitors for Th17? Bettelli, E & Kuchroo, V.K. J. Exp. Med. 201:169-171, 2005 Influence of Co-stimulatory Molecules on Differentiation Th1 IL-2 IFNg IL-2 LT (TNFb) ThP Th2 IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 Th1 cell Transcription Factors Szabo, S, Cell 100:655, 2000 Influence of Transcription Factors on Th2 Cell Differentiation IL-12R Th2 IL-4R IL-4 APC TCR IL-12 STAT6 GATA-3 IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 C-maf (IL-4 transcription factor) NFAT CD4 cell Expression of GATA-3 During Th2 Cell Differentiation Immunity 9:745, 1998 Epigenetic Regulation of T cell Differentiation JCI 109:431, 2002 Nucleosomes/Histones Acetylated Methylated Phosphorylated T helper Cell Differentiation type 1 IFNs IL-23 IL-27 IFNg IL-12 IL-12R IL-18R DC DC IL-10 IFNgR STAT1 T-BET STAT4 NFkB IFNg IL-4 TCR c-maf IL-4R STAT6 GATA-3 IL-4 A Dominant Th1 vs. Th2 Response Alters the Outcome of Infection A Dominant Th1 vs. Th2 Response Alters the Outcome of Infection Th1/Th2 Differentiation is linked to cell division Immunity 9:229, 1998 Papers for Discussion 5/12/05 P1. 1). Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD, Cua DJ.Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2003 Dec 15;198(12):1951-7. P2. Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005 Jan 17;201(2):233-40.