* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classes of effector CD4 + T cells Development of Th1 cells
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
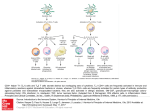
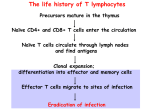
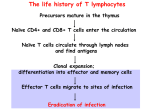
EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF HELPER T-LYMPHOCYTES Phases of T cell responses Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2014 Elservier Naive helper T cells encounter antigen during their recirculation through secondary lymphoid organs Classes of effector CD4+ T cells Differentiation of Th subsets from naïve CD4+ T cells: general principles I. • Different subsets develop from the same naïve CD4+ T cells. • Cytokines produced at the site of antigen recognition drive differentiation into one or the other subset. • The cytokines that drive the development of CD4+ T cell subsets are produced by APCs (primarily dendritic cells and macrophages) and other immune cells (such as NK cells and basophils or mast cells) present in the lymphoid organ where the immune response is initiated. Differentiation of Th subsets from naïve CD4+ T cells: general principles II. • Stimuli other than cytokines may also influence the pattern of helper T cell differentiation. • Differentiation of each subset is induced by the types of microbes that the subset is best able to combat. • Commitment to each subset is driven by transcription factors. • Each subset of differentiated effector cells produces cytokines that promote its own development and may suppress the development of the other subsets. Classes of effector CD4 + T cells Molecular events in follicular helper T cell generation Diversity of follicular helper T cells (Tfh) Follicular helper T cells (Tfh) • Some effector T cells express the chemokine receptor CXCR5, migrate to lymphoid follicles, and help B cells (isotype switching, affinity maturation) • Characteristics of Tfh: – Surface expression of CXCR5, ICOS – Transcription factor: BCL-6 – Cytokines secreted: IL-21 + IL-4 or IFNγ (or IL-17?) Sequence of events in the reactions of effector CD4+ T cells in the peripheral tissues Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2014 Elservier Classes of effector CD4 + T cells Development of Th1 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Functions of Th1 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Effector functions of Th1 cells Activation Killing Proliferation Feed back Entry to tissue Recruitment Macrophage activation by Th1 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Th1 cells • Th1 differentiation is driven mainly by the cytokines IL-12 and IFN-γ and occurs in response to microbes that infect macrophages. • IFN-γ and IL-12 stimulate Th1 differentiation by activating the transcription factors T-bet, STAT1, and STAT4. • The principal function of Th1 cells is to activate macrophages to ingest and destroy microbes. - Classical macrophage activation - Enhance of MHC-associated antigen presentation Classes of effector CD4 + T cells Development of Th2 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Functions of Th2 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Classical and alternative macrophage activation Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Th2 cells • Th2 differentiation is stimulated by the cytokine IL-4 and occurs in response to helminths and allergens. • IL-4 stimulates Th2 development by activating the transcription factor STAT6, which, together with TCR signals, induces expression of GATA-3. • Th2 cells stimulate IgE-, mast cell- and eosinophil-mediated reactions that serve to eradicate helminthic infections. - Activation of mast cells and eosinophils - Host defense at mucosal barriers - Alternative macrophage activation Classes of effector CD4 + T cells Development of Th17 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Functions of Th17 cells Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th ed., 2015 Elservier Th17 cells • The development of Th17 cells is stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines produced in response to bacteria and fungi. • The development of Th17 cells is dependent on the transcription factors RORγt and STAT3. • The principal effector function of Th17 cells is to help the destroy of extracellular bacteria and fungi, mainly by inducing neutrophilic inflammation. • Th1 and Th17 cells function cooperatively in phagocyte-mediated elimination of microbes in cell-mediated immunity. • Th17 cells contribute to the pathogenesis of many inflammatory diseases. (MS, IBD, RA, psoriasis) Functional classes of effector CD4 T cells Genetic proof for the importance of different T cell subsets in humans • Mutations affecting IL-12/IFN-γ cytokines or receptors → defective Th1 responses → atypical mycobacterial infections • Mutations affecting Th17 development or IL-17 → mucocutaneous candidiasis and bacterial abscesses (Job’s syndrome)