* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download latent
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Environment and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Dimensional models of personality disorders wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Ego-dystonic sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Political psychology wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Relationship counseling wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Ego psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological injury wikipedia , lookup
Personality psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Lifetrack Therapy wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Hypostatic model of personality wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Hidden personality wikipedia , lookup
Freud's psychoanalytic theories wikipedia , lookup
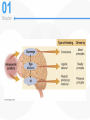
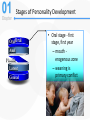
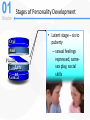
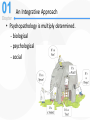
Chapter 1 Abnormal Behavior in Historical Context Psychological Disorder What Is a Psychological Disorder? • Psychological dysfunction – Breakdown in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral functioning • Personal distress – Difficulty performing appropriate and expected roles – Impairment is set in the context of a person’s background • Atypical or not culturally expected response – Reaction is outside cultural norms Abnormal Behavior Defined • An accepted definition – A psychological dysfunction associated with distress or impairment in functioning that is not typical or culturally expected • The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSMIV-TR) – Contains diagnostic criteria • Psychopathology – The scientific study of psychological disorders The Science of Psychopathology • Mental health professionals – The Ph.D.: Clinical and counseling psychologist – The Psy.D.: Clinical and counseling “Doctor of Psychology” – The Ed.D.: Clinical and counseling “Doctor of Education – M.D.: Psychiatrist – Psychiatric social worker – Psychiatric nurse – Family therapists; mental health counselors Scientist – practitioner model Clinical Description • Begins with the presenting problem • Description aims to: – Distinguish clinically significant dysfunction from common human experience • Describe prevalence and incidence of disorders - sex ratio - age of onset Clinical Description • Describe onset of disorders –Acute vs. insidious onset • Describe course of disorders –Episodic, time-limited, or chronic course • Prognosis –Good vs. guarded Causation, Treatment, and Outcome • Etiology – What contributes to the development of psychopathology? • Treatment development – How can we help alleviate psychological suffering? – Includes pharmacologic, psychosocial, and/or combined treatments Historical Conceptions of Abnormal Behavior • Existed in all cultures and across all time periods. • Causes and treatment of abnormal behavior vary widely across cultures and time periods. • Three dominant traditions – Supernatural – Biological – Psychological The Supernatural Tradition • Deviant behavior as a battle of “Good” vs. Evil – Caused by demonic possession, witchcraft, sorcery – Treatments included exorcism, torture, beatings, trephining, and shock therapy The Supernatural Tradition • Mass hysteria (rave without music) – Emotion contagion – Mob psychology • The moon and the stars (astrology) – lunacy • Hippocrates: Abnormal behavior as a physical disease - hysteria” = wandering uterus • “Galen extends Hippocrates’ work – Humoral theory of mental illness – linked abnormality with brain chemical imbalances The 19th Century • General paresis (syphilis) and the biological link with madness – Several unusual psychological and behavioral symptoms – Pasteur discovered the cause – a bacterial microorganism – Led to penicillin as a successful treatment – Bolstered the view that mental illness = physical illness • John P. Grey – treatment includes rest, diet, ventilation and improved hospitals Consequences of the Biological Tradition • Mental illness = physical illness • Emil Kraepelin (1856-1926) – Diagnosis and classification The Psychological Tradition • The rise of moral therapy – More humane treatment of institutionalized patients – Encouraged and reinforced social interaction The Psychological Tradition • Proponents of moral therapy – Philippe Pinel and Jean-Baptiste Pussin – Benjamin Rush – led reforms in U.S. – Dorothea Dix – mental hygiene movement • Asylum reform and the decline of moral therapy • Emergence of competing alternative psychological models Freud’s Psychoanalysis • Psychoanalysis – Freud’s theory of personality and therapy based on it Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) LO 13.2 How did Freud’s view form the basis for psychodynamic theory? • Founder psychoanalytic movement • Cultural background – Victorian era • sexual repression, sex for procreation, mistresses satisfied men’s “uncontrollable” sexual desires Personality • Freud proposed that excessive anxiety might be due to: • Lack of sexual gratification • Masturbation • Traumatic sexual experiences from early childhood 21 The Unconscious Mind Divisions of The Personality Ego Superego ID Id, Ego and Superego Id unconscious sexual and aggressive drives operating on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification. Superego provides standards for judgment (the conscience) acts as a moral center Largely conscious, ego functions as the “executive” and mediates the demands of id and superego – reality principle. 24 Exploring the Unconscious The process of free association (chain of thoughts) leads to painful, embarrassing unconscious memories 26 Freudian slip – a slip of the tongue that reveals an unconscious motive or thought “Freud gave 5 pubic lectures here.” Dream Analysis Another method to analyze the unconscious mind is through interpreting the manifest and latent contents of dreams. The Nightmare, Henry Fuseli (1791) 29 Rorschach Inkblot Test 10 inkblots - designed by Hermann Rorschach. It seeks to identify people’s inner feelings by analyzing their interpretations of the blots. Lew Merrim/ Photo Researcher, Inc. 30 Thematic Apperception Test TAT) Developed by Henry Murray, TAT is a projective test in which people express their inner feelings about ambiguous scenes. Lew Merrim/ Photo Researcher, Inc. 31 Defense Mechanisms • Defense mechanisms - unconscious distortions of perceptions to reduce anxiety – Repression - refuse to consciously remember a threatening or unacceptable event – Denial - refuse to acknowledge threatening situation – Rationalization - invent acceptable excuses for unacceptable behavior Defense Mechanisms (cont) – Projection - unacceptable impulses seen as originating in someone else – Reaction formation - opposite emotional or behavioral reaction to way one really feels – Displacement - redirect feelings from a threatening target to less threatening one Defense Mechanisms (cont) – Regression - fall back on childlike response patterns when under stress – Identification - try to become like someone else to deal with anxiety – Compensation - make up for inferiorities in one area by becoming superior in another area – Sublimation - channel socially unacceptable impulses into socially acceptable behavior Stages of Personality Development • Fixation – unresolved psychosexual stage conflict – “stuck” in stage relevant personality traits and behaviors • Psychosexual stages - five stages of personality tied to sexual development Stages of Personality Development OralOral Anal Phallic Latent Genital • Oral stage - first stage, first year – mouth erogenous zone – weaning is primary conflict Stages of Personality Development Oral AnalAnal Phallic Latent Genital • Anal stage – one to three years, ego develops – toilet training conflict – expulsive vs. retentive personalities Stages of Personality Development Oral Anal PhallicPhal lic Latent Genital Phallic stage – three to six years, superego develops – sexual feelings – Oedipus complex - Electra complex Identification Through identification their superego gains strength incorporating parents’ values. 39 Stages of Personality Development Oral Anal Phallic Late Latent nt Genital • Latent stage – six to puberty – sexual feelings repressed, samesex play, social skills Stages of Personality Development Oral Anal Phallic Latent Genital Genital • Genital stage – puberty – sexual feelings consciously expressed Modern Psychoanalytic Theory LO 13.4 How does modern psychoanalytic theory differ from that of Freud? • Current research has found support for… – defense mechanisms – concept of unconscious mind that can influence conscious behavior Later Developments in Psychoanalytic Thought • Anna Freud and self-psychology – Emphasized influence of the ego in defining behavior • Melanie Klein, Otto Kernberg, and object relations theory – Emphasized how children incorporate (introject) objects – Objects – images, memories, and values of significant others Later Developments in Psychoanalytic Thought (continued) • The “Neo-Freudians”: Departures from Freudian thought – De-emphasized the sexual core of Freud’s theory – Jung, Adler, Horney, Fromm, and Erickson © 2006 The McGrawHill Companie s, Inc. All rights reserved. Santrock, Education al Psycholog y, Second Edition, Classroom Update 3) The Humanistic Perspective a)personal growth b)freedom to choose c) being sensitive to others Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) Carl Rogers (1902-1987) © 2006 The McGrawHill Companie s, Inc. All rights reserved. Santrock, Education al Psycholog y, Second Edition, Classroom Update Being (growth) Needs Deficiency Needs Self- Actualization © 2006 The McGrawHill Companie s, Inc. All rights reserved. Santrock, Education al Psycholog y, Second Edition, Classroom Update • the self-actualized individual: • An ability to perceive reality accurately • Independence, spontaneity, and creativity • Treating others with unconditional positive regard • An outlook that emphasizes problem-solving • Enjoyment of life • A good sense of humor Humanistic Theory • Person-centered therapy – Therapist conveys empathy and unconditional positive regard – Minimal therapist interpretation • There is no strong evidence that humanistic therapies work. The Behavioral Model • Derived from a scientific approach to the study of psychopathology • Classical conditioning (Pavlov; Watson) – Ubiquitous form of learning – Contingency between neutral and unconditioned stimuli – Conditioning was extended to the acquisition of fear John B. Watson (1878-1958) The Beginnings of Behavior Therapy • Challenged psychoanalysis and non-scientific approaches • Early pioneers – Joseph Wolpe – systematic desensitization • Operant conditioning (Thorndike; Skinner) – Reinforcement – Another ubiquitous form of learning – Voluntary behavior is controlled by consequences B. F. Skinner (1904-1990) The Beginnings of Behavior Therapy • Learning traditions influenced the development of behavior therapy. – Behavior therapy tends to be time-limited and direct – Strong evidence supporting the efficacy of behavior therapies An Integrative Approach • Psychopathology is multiply determined. - biological - psychological - social An Integrative Approach • Defining abnormal behavior – Complex, multifaceted, and has evolved • The supernatural tradition – Has no place in a science of abnormal behavior