* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Discovery of the Cell
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
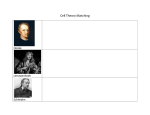
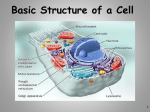
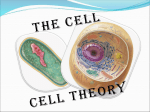
The Discovery of the Cell A history lesson Robert Hooke The English scientist Robert Hooke, who studied the cork with a crude microscope, first described cells in 1665. He thought the cork structures looked like the cells that the monks lived in so he called them a cell Scanning electron of a wood Cell History The Dutch scientist Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living cells in detail in the 1670s. With the use of a basic microscope he was able to see things too small with the naked eye. Known as "the Father of Microbiology" Cell Theory In 1839, German scientist Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann formulated the cell theory. Noticing a similarity between plant and animal cells, they stated that all living organisms consist of cells and cell products. Thus, a whole organism could be understood through the study of its cellular parts Cell theory Cell reproduction history In 1858 the German pathologist Rudolf Virchow's theory, that all cells come from preexisting cells, this led to the development of cell division and cell differentiation. He corrected Schwaan and Schleider.