* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Analytical chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Destruction of Syria's chemical weapons wikipedia , lookup
Chemical warfare wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
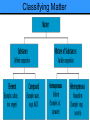
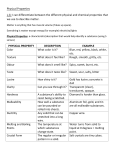
Chemistry The study of the composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass The amount of matter an object contains. Physical State (see Table 2.2) • Solid: definite shape and volume • Liquid: Takes on shape of container, definite volume • Gas: Fills any space; compressible Gas vs. Vapor A vapor is the gaseous state of a substance that is generally a liquid or solid at room temperature (i.e.water vapor). Classifying Matter Substance Matter with a uniform and definite composition (also called a pure substance). All samples of a substance have identical physical properties. Elements • Simplest forms of matter. • Building blocks for all other substances. • Cannot be separated by chemical means. • Represented by a one- or two-letter chemical symbol. Hg Compounds Can be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. NaCl CaCO3 Physical Property- quality or condition that can be observed or measured without changing the substance’s composition. For example: • • • • • • • Color Solubility Hardness Density Melting point Boiling point Physical state INTENSIVE physical property Does NOT depend on the amount of material present (e.g. color, melting point, freezing point, density) EXTENSIVE physical property DOES depend on the amount of material present (e.g. mass, volume) Physical Change- Alters a given material without changing its composition. • Cutting • Grinding • Bending • Melting • Boiling • Freezing Mixture A physical blend of two or more substances. Can be separated by physical means. Compositions may vary. Homogeneous Mixture Completely uniform composition. Also known as a solution. Substances can be either Element OR Compound C Al2O3-Cr Heterogeneous Mixture Not uniform in composition. Chemical Reaction One or more substances change into new substances Reactants Starting substances in a chemical reaction. Products Resulting substances in a chemical reaction. Chemical Property The ability of a substance to undergo chemical reactions and to form new substances. Chemical Changes • Result in a change of chemical composition of the substances involved. • Most chemical changes are not easily reversed. • Ex: Rust, Burn, Rot, Explode, Corrode Law of Conservation of Mass • In any physical change or chemical reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed. • The mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants.