* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypothalamus
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
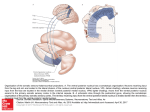
Diencephalon: Thalamus and Hypothalamus Diencephalon • Relay between the brainstem & cerebral cortex • Dorsal-posterior structures – Epithalamus • Habenular nuclei – integrate smell & emotions • Pineal gland – monitors diurnal / nocturnal rhythm – Thalamus – Metathalamus • Medial geniculate body – auditory relay • Lateral geniculate body – visual relay • Ventral-anterior structure – Hypothalamus Position Position: Lies between midbrian and cerebrum, almost entirely surrounded by cerebral hemisphere Subdivision Doral thalamus Metathalamus Epithalamus Subthalamus Hypothalamus lateral ventricle third ventricle Anterior Commissure Interventricular foramen Optic tract Click ! ( foramen of Monro ) Lamina Terminaris Mammillary Body Infundibulum Sulcus terminalis Stria terminalis terminal vien Anterior thalamic tubercle Anterior thalamic nucleus sulcus Ant. tubercle Stria medullaris thalami Massa intermedia ( interthalamic adhesion ) Hypothalamic sulcus Hypothalamus Posterior Commissure Habenula trigone Habenula nucleus Mammillary body Optic chiasm infundibulum Turber cinereum Dorsal thalamus External features A large egg-shaped nucleus mass, Anterior end called anterior thalamic tubercle, Posterior end called pulvinar Right and left portion of thalamus are joined by interthalamic adhesion Floor-hypothalamic sulcus Subdivision Principal Nuclei Common abbreviation Ant. nuclear group Med. nuclear group Lat. nuclear group Dorsal tier Lateral dorsal LD Lateral posterior LP Pulvinar Ventral tier Ventral anterior VA Ventral lateral VI Ventral posterior VP Ventral posterolateral VPL Ventral posteromedial VPM Classification of nuclei of dorsal thalamus Three nuclear group divided by internal medullary lamina Anterior nuclear group Medial nuclear group Lateral nuclear group internal medullary lamina Med. nuclear group Dorsal tier Ant. nuclear group Pulvinar Medial geniculate body (MGN) Ventral anterior Ventral lateral Ventral posterior nucleus (VP) Lateral geniculate body (LGN) Ventral posterolateral (VPL) Ventral posteromedial (VPM ) Function of the Thalamus • Sensory relay – ALL sensory information (except smell) • Motor integration – Input from cortex, cerebellum and basal ganglia • Arousal – Part of reticular activating system • Pain modulation – All nociceptive information • Memory & behavior – Lesions are disruptive Input to the Thalamus Input to the Thalamus Metathalamus Vision and Hearing Input to the Thalamus Sensory relay - Ventral posterior group all sensation from body and head, including pain Input to the Thalamus Motor control and integration Projections from the Thalamus Behavior and emotion connection with hypothalamus Special relay nuclei Vent. lateral (VL) Receiving dentate nucleus to motor cortex Vent. anterior nucleus (VA) Receiving globus pallidus and substantia nigra to motor cortex Vent. posteromedial nucleus (VPM) -receives trigeminal lemniscus and taste fibers Vent. posterolateral nucleus (VPL) receives medial lemniscus and spinal lemniscus Projects to first somatic sensory area via central thalamic radiation Medial, lateral geniculate bodies Thalamus: coronal view Dorsomedial nucleus has reciprocal connections to prefrontal cortex. Concerned with judgment, decision making, memory and behavior. Mediodorsal nucleus Internal capsule Thalamus Ventral lateral nucleus Mediodorsal nucleus VL nucleus has reciprocal connections with primary motor cortex. It receives input from cerebellar nuclei. With VA nucleus (which receives input from basal ganglia) contributes to planning and control of movement. Internal capsule Metathalamus Lateral geniculate body (LGN) Medial geniculate body (MGN) Metathalamus Metathalamus Medial geniculate body (MGN) Relay station of audition Receive fibers from inferior colliculus Projects to auditory area via acoustic radiation Lateral geniculate body (LGN) Relay station of vision Receive fibers from optic tract Projects to visual area via optic radiation Functional subdivisions Nonspecific relay nuclei receive input from many converging sources and in turn project widely to the association areas of cerebral cortex Anterior nuclear group Medial nuclear group(mediodorsal) Dorsal tier of lateral nuclear group Association nuclei(reticular nuclei) receive afferents from rhinencephalon and reticular formation of brain stem, project mainly to hypothalamus and corpus striatum Midline nucleus group(interthalamic connection): visceral afferent , hypothalamus Intralaminar nuclear group (centromedian): pain, consciousness Thalamic reticular nucleus Thalamus: axial view Descending upper motor neurons Cerebral peduncles Internal capsule Thalamus: axial view Thalamus: Pons sagittal view Thalamus: sagittal view Thalamus: coronal view Thalamus: coronal view 3rd ventricle Thalamus: coronal view Internal capsule Thalamus: coronal view Cerebral peduncles Internal capsule Thalamus: blood supply Corona Radiata & Internal capsule Int. Capsule: Thalamic radiation, pyramidal & extrapyramidal Subthalamus Transition zone between diencephalons and tegmentum of midbrain Contain subthalamic nucleus, parts of red nucleus and substantia nigra, zona incerta Epithalamus Includes Thalamic medullary stria Habenular trigone Habenular commissure Pineal body posterior commissure Hypothalamus Position-lies ventral to thalamus Boundaries Superiorly: hypothalamic sulcus Inferiorly: optic chiasma tuber cinereum Infundibulum mamillary body Anterior: lamina terminalis Posterior: continues with midbrain tegmentum Paraventricular nucleus Paraventriculohypophyeal tract Supraoptic nucleus Supraopticohypophyseal tract Mamillary nucleus arcuate nucleus tuberoinfundibular tract infundibulum anterior lobe of hypophsis posterior lobe of hypophysis Hypothalamus THE HYPOTHALAMUS Lateral zone No discrete nuclei Regulation of food and water intake •Medial zone Tuberal region (middle reg.) VM – satiety center (lesion produces hyperphagia + obesity) Arcuate nc. - delivers peptides to the portal vessels •Well defined nuclei •Chiasmatic region (anterior region) Mamillary region (posterior reg.) •hormone release- (SO,PV) •Cardiovascular function (Ant.) •Circadian rhytms (SCH) •Body temperature (Preoptic nc.) Posterior nc.- elevating of blood pressure, pupillary dilatation, body heat conservation Mammillary ncc. – memory formation (fornix) Hypothalamus: sagittal view Hypothalamus --connection Connects with limbic system Connects with brainstem and spinal cord Connects with dorsal thalamus Connects with hypophysis Hypothalamus --connection Supraoptic nucleus →supraoptic nucleus (ADH) →supraopticohypophyseal tract →posterior lobe of hypophysis Paraventricular nucleus → paraventicular nucleus (oxytocin) →paraventriculohypophyseal tract→posterior lobe of hypophysis Paraventricular nucleus Paraventriculohypophyseal tract Supraoptic nucleus Supraopticohypophyseal trac Inferior hypophyseal a. posterior lobe of hypophysis Hypophyseal v. Parvicellular neurons in the arcuate nucleus and nearby region of the walls of the third ventricle secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones → tuberoinfundibular tract →portal vein of hypophsis → anterior lobe of hypophsis Tuberoinfundibular tract Median eminence Portal v. Superior hypophyseal a. anterior lobe Hypophyseal v. Hypothalamus: coronal view Pre-Optic Region Gonadotropic releasing hormone Sexual arousal, appetite, reproduction Hypothalamus: coronal view Suprachiasmic Region Secrete ADH, oxytocin Transported via axons to posterior pituitary (hypophysis) Hypothalamus: coronal view Regulates thirst Hypothalamus: coronal view Body temperature Circadian rhythms Hypothalamus: coronal view Tuberal Region Satiety Hypothalamus: coronal view Regulates prolactin and growth hormone β endorphin for pain Hypothalamus: coronal view Mammillary region Limbic system Hypothalamus: coronal view Hypocretin (orexin) Narcolepsy, reward