* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
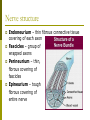
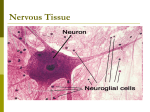
Nervous System Transmits information from 1 part of the body to another, rapid communication 2 major divisions Central Nervous system (CNS)– brain and spinal cord Peripheral (PNS)– nerves of the body Autonomic nervous system (ANS)– regulates involuntary functions Cells of nervous system Neurons – made of dendrites, cell body, axons Dendrites – take information to cell body Axons – take information away from cell body 3 types of neurons Sensory – to brain or spinal cord (afferent) Motor – away from brain/spinal cord (efferent) Interneuron – conduct impulses from sensory to motor neurons. Structure of neuron See handout Myelin – white fatty substance that covers some axons outside of CNS Schwann cell – forms myelin Nodes of Ranvier – indentions between schwann cells Neurilemma – outer cell membrane of a schwann cell Neuroglia cells (glia) Support cells for neurons, do not transmit impulses. 3 types of glia Astrocytes – star like extensions that hold neurons and blood vessels together. Microglia – small, used as microphages (microbe eating scavengers) Oligodendrocytes – hold nerve fibers together and produce fatty myelin sheath that envelops nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord (instead of schwann cells) Disorders of nervous tissue Neuromas – tumors of nervous system, seen mostly in glia cells (glioma) Multiple neurofibromatosis – inherited Numerous fibrous neuromas Multiple sclerosis – (CNS) disorder of oligodendroglia Myelin lost and destroyed becomes plaque like lesions Nerve conduction impaired Nerves – see figure 9-6 Group of peripheral nerve fibers (axons) in PNS Look white, covered in myelin CNS – called “tracts”, White matter – part of CNS covered in myelin, axons Grey matter – dendrites and cell bodies not covered in myelin sheath Nerve structure Endoneurium – thin fibrous connective tissue covering of each axon Fascicles – group of wrapped axons Perineurium – thin, fibrous covering of fascicles Epineurium – tough fibrous covering of entire nerve Reflex arc Specialized type of neuron pathway that nerve impulses travel 2 neuron arc, simplest, ex – knee jerk 3 neuron arc, ex. Withdrawal reflex impulse ->receptor (end of dendrite) -> sensory neuron ->cell body (ganglion)-> axon-> synapse ->chemicals sent across gap ->dendrite -> cell body (ganglion) -> axon of motor neuron -> creates reflex. Nerve impulses Self propagating wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron’s plasma membrane. Must be initiated by a stimulus (pressure… At rest, the membrane has slightly + charge (Na+) outside and – inside When stimulated, inside membrane becomes + and – outside temporarily. Impulses travel in 1 direction across neurons surface. Saltatory conduction – faster impulses when nerve has myelin covering.