* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENVI 30 Environmental Issues
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
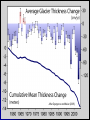
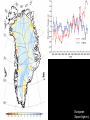
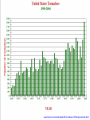
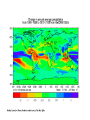
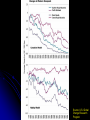
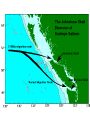
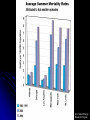
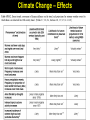
Climate Change – Effects I. A. Sea Level Rise • Warming Ice Melt Sea Level Rise • • • Since 1880, sea level rising ~15 cm century-1 • • • Increased conversion of ice to water Thermal expansion Accelerated since 1940s Melting of all ice should lead to sea level rise of ~70 m Lomborg – More affluent world should lead to more protection against effects of sea level rise http://www.grida.no/climate/vital/19.htm Climate Change – Effects I. B. Reduced Ice/Snow Cover • • Temperate/Tropical glaciers Polar ice caps Holgate Glacier, AK 1909 vs. 2004 Muir Glacier, AK 1941 vs. 2004 After Dyurgerov and Meier (2005) SAHFOS European Space Agency III. Climate Change – Effects C. Extreme Weather • More and more severe • • • Tropical storms Tornadoes Increasing economic losses • Lomborg – Changing population patterns, demography, economic prosperity www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/climate/research/cei/cei.html www.hprcc.unl.edu/nebraska/US-tornadoes-1953to-present-bar.html Climate Change – Effects I. D. Precipitation Patterns • Warming should lead to • • • Reduced precipitation at low latitudes Increased precipitation at high latitudes Examples • • • Drought in many parts of the world Reduced snowpack in Sierra Nevada Mountains due to rainfall instead of snow Increased agricultural production in some areas • Combined with higher temperatures and [CO2] 20th Century Source: U.S. Global Change Research Program Source: U.S. Global Change Research Program Climate Change – Effects I. E. Ozone Holes • Global warming of the atmosphere translates to stratospheric cooling • Stratospheric cooling may enhance ozone destruction in Antarctic and make phenomenon more common in Arctic (Waibel et al. 1999) Climate Change – Effects I. F. Ecosystem Effects • Expand ranges of warmth-tolerant species and contract ranges of warmth-intolerant species • • • Within an ecosystem, some species more sensitive to climate change than others • • • • Colder-living species might be displaced poleward as well as upward in elevation Species unable to adapt or move would go extinct Species composition of communities almost certainly will change Ex: Intertidal (Pacific Grove – Central CA) • Significant abundance changes in 32/45 species between 1931 and 1994 • 8/9 southern species increased significantly • 5/8 northern species decreased significantly Changes in CO2 concentration lower pH of ocean Behavioral changes (Ex: Sockeye salmon) I. Climate Change – Effects G. Health • Consistently elevated temperatures can lead to immunosuppression • • • Exacerbated by elevated levels of UV-B Allergies could worsen due to increased pollen production (heat), dust (drought), mold (humidity) Additional human mortality from severe summer heat U.S. Global Change Research Program Climate Change – Effects I. H. Tropical Pests and Diseases • Many tropical diseases transmitted by animal vectors – insects, rodents Concern that global warming could increase geographic ranges of vectors • a. • • • Dengue fever Ex: 1995 – Rising temperatures allowed a coastal mosquito species to cross mountains and spread across Costa Rica, carrying dengue fever Reached as far north as Texas border 140,000+ people infected; 4000+ died Climate Change – Effects I. H. Tropical Pests and Diseases b. • • • • • Malaria Most prevalent vector-borne disease (1-2 million cases/year) Transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes Warming could lead to • Broader geographic range (estimate that +2oC could expand range from 42 to 60% of land area) • Higher metabolic rate More food • Faster maturation More rapid reproduction • Faster parasite life cycle Potential spread into large urban areas (Nairobi, Kenya; Harare, Zimbabwe) with immunologically naïve pop’ns Projections are controversial and highly variable Climate Change – Effects