* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch12 Climate Change and Humans
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Decarbonisation measures in proposed UK electricity market reform wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
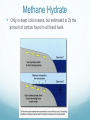
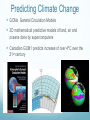
Ch12 Climate Change and Humans Can we reduce our impact on the biosphere and still meet human needs? How does global warming affect the polar bear? Seals are a very important part of their springtime diet. Getting seals is totally dependent on a strong ice pack reaching the shore. With global warming the pack ice reaches shore lots fewer days = less seal hunting Polar bears are showing signs of not enough to eat – they are getting smaller and leaner Natural Greenhouse Effect… Is why there is life on earth! Not NOT caused by humans. 65% of re-radiation of sun’s back to Earth occurs owing to H2O VAPOR. heat naturally This is STILL THE MOST ABUNDANT GREENHOUSE GAS Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Extra green house effect caused by human activity Greenhouse Gases 1. Water vapor ( contributes 65% of re-radiation) 2. carbon dioxide (contributes 25% of re-radiation) 3. methane 4. nitrous oxides 5. halocarbons (i.e. CFCs) 6. others Human produced GGs Global warming potential of a greenhouse gas depends on: 1. Amount of gas entering atmosphere/year 2. Lifetime of gas in atmosphere 3. Effects of gas on atmospheric chemistry 4. Effect of gas on other atmospheric gases Carbon Dioxide Most abundant greenhouse gas that contributes to the ENHANCED greenhouse effect Found in: Atmosphere Fossil Fuels Carbonates in limestone, shells and Earth’s crust Hydrocarbons in oil and natural gas Organic compounds in live and decaying organisms Hydrogen carbonates dissolved in water The Carbon Cycle Most carbon is in: Soils, fossil fuels and cement Surface Ocean Deep Ocean Carbon sinks i.e. fossil fuels, forests, soil, oceans, are reservoirs of carbon and CO2 and keep it cycling and out of atmosphere Environmental Concerns LEVELS OF ATMOSPHERIC CO2 ARE 37% HIGHER THAN IN 1750 75% OF THIS INCREASE HAS OCCURRED IN THE LAST 75 YEARS CAN LIFE ADAPT TO THIS RAPID RATE OF CHANGE???? Other Greenhouse Gases of Concern Methane – CH4 Called natural gas because produced by bacterial decay of organic matter Of concern because it has global warming potential 25x that of CO2 Methane Used for heating homes and buildings, generates electricity Concentration in atmosphere 146% since 1800 Trash generator Cow-poop generator! Methane Hydrate Only in deep cold oceans, but estimated to 2x the amount of carbon found in all fossil fuels. Nitrous Oxide Concern: Has global warming potential 300x that of CO2 From bacterial breakdown of fertilizers, and burning of fossil fuels at very high temperatures Halocarbons Carbon compounds containing halogens (Cl, F, Br) i,e, CFCs…… Used for refrigerants, coolants, fire extinguishing ; Concern: thin the ozone layer, global warming potential is 12000 to 15000x greater than CO2 Human effect on Global Climate Change DEFORESTATION = Increases Global warming 25% of global CO2 emissions Forests are important since they absorb radiation and cool surrounding area Forests remove atmospheric CO2 for Photosynthesis CITIES = urban heat islands, increase atmospheric temperature Predicting Climate Change GCMs General Circulation Models 3D mathematical predictive models of land, air and oceans done by supercomputers Canadian GCM1 predicts increase of over 4oC over the 21st century Factors influencing future greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Future human population growth Energy use per person Types of energy used and amount of greenhouse gases each energy type generates Choices we make Natural events: i.e volcanic eruptions If CO2 emissions doubled what will happen to Canadian biomes? Tundra and Taiga range will Temperate deciduous forest, grasslands and desert ranges will What can we do? How can we reduce our impact on the biosphere and still meet human needs?