* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification_of_Living_Things_1.3C
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
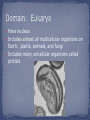
Chapter 1.3C Organisms are classified by their cell type. Scientists have identified three main domains. A domain is a broad category of living things that is based on characteristics of their cells. Prokaryotic Unicellular Simple structure Cell Wall Able to live in extreme conditions (extreme heat, little oxygen) Genetically different from bacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Simple structure Cell Wall Have nucleus Includes almost all multicellular organisms on Earth: plants, animals, and fungi Includes many unicellular organisms called protists Animal Kingdom: invertebrates, vertebrates, multicellular, no cell walls, obtain energy through respiration Plant Kingdom: multicellular, have cell walls, obtain energy through photosynthesis (ex: mosses, ferns, flowering and seed plants) Fungi Kingdom: Cells with cell walls but not green and do not carry out photosynthesis, break down other organic materials to obtain food (ex: mushrooms, mold, yeast) Protist Kingdom: come in a wide variety of forms, some are animal-like, such as amoeba, paramecium and protozoan. Some are plant-like, such as algae, and others are fungi-like. Many are single-celled and others are multicellular. Monera Kingdom: Some photosynthesize while others respire. The nucleus of moneran cells are not bounded by nuclear membranes like cells in other kingdoms. (ex: bacteria and blue-green algae) Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Cordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primata Family: Hominadae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens (note: species is not capitalized) The two part naming system is called binomial nomenclature.