* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Microscopes
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
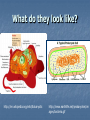
Types of Microscopes Types of Microscopes Light Microscope: what we use in lab Uses light to magnify Used to look at living cells Magnify: up to 1500x Electron Microscope: (1930-1940) Uses beams of electrons Magnify: up to 500,000x See inside of cells, look at structures 2 types Scanning Electron Microscope: (SEM) Scan surfaces of cells, look at 3D shape http://www.mos.org/sln/sem/diatom.html http://mse.iastate.edu/microscopy/whatsem.html Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Look at structures within the cell http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_electron_microscope New Technology New models & helpful techniques all the time Example: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Uses flow of electrons to create computer images of atoms on the surface of a molecule www.chem.utoronto.ca/staff/DHIRANI/index.htm Cell Theory The Cell Theory: 3 Main Ideas: All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure & organization of organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. 1. The Cell: With better microscopes, discovered that cells contain small specialized structures called organelles Each organelle has a specific function within a cell Types of Cells: 2 broad groups: 1. Eukaryotes: contain membrane-bounded organelles 2. Most multi-cellular organisms & some unicellular ones, like algae Prokaryotes: do not Example: bacteria and other unicellular organisms What do they look like? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryotic http://www.earthlife.net/prokaryotes/im ages/bacteria.gif