* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View Powerpoint Presentation - Northeast Biomanufacturing Center
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
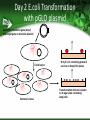
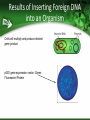
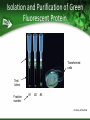
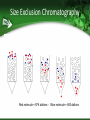
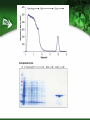
How to Start a Biotechnology Program Mary Jane Kurtz, Ph.D NBC2 Consultant [email protected] Why Biotechnology? A number of good reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. Academics Technical skills Biotechnology as a future career Biotechnology is exciting Biology can be seen with a molecular perspective Can answer questions about ourselves Can provide new medical aid to the afflicted Getting Support from Your Administration This is important to the future success of your new program Allows for obtaining outreach to new students, space to grow, and expenses for needed equipment Supports the teachers who are involved in program Academic Advantages Allows students to do up-to-date hands-on experiments Demonstrates the integration of all sciences, math, and engineering through experiences in the laboratory It develops writing skills for clarity, focus and documentation Technical Advantages Curriculum can introduce career tracks for students in a developing scientific area Using hands-on activities, students have a opportunity to develop skills needed in the workplace at all levels of formal training Potential career paths flowing from the knowledge gained is broad based Biomanufacturing Curriculum: National Standard Concepts Covered • Math, Biology, Chemistry in Curriculum – – – – Measurement Solutions Enzyme reactions Transformation of cells with DNA – Forces used in centrifugation, electrophoresis etc. • National Academy of Sciences Standards – Unit of Math & Science – Structure/properties of matter – Chemical reactions/conservation of matter – Cell structure and functions, heredity – Motions and forces Biotechnology A plus for Teachers and Students Integrated science education: Science Technology Engineering and Math (STEM) Career pathways towards work/school focused on science with thousands of new jobs predicted in the next few years Laboratory based activities = increased interest – More exciting ways of introducing concepts – Hands-on learning is more inclusive – State-of-the-art laboratories Biomanufacturing vs Biotechnology Offers diverse career pathways Hands-on learning of science Understanding of good laboratory practices Stability in career pathways Assistance in obtaining college degrees through company support Both highly academic and technically oriented students Ten Technician Jobs Anchor Ten Biomanufacturing Departments • Facilities/Metrology • Validation • Environmental Health and Safety (EH&S) • QA • Upstream Processing • Downstream Processing • QC Microbiology • QC Biochemistry • Process Development RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT(pre-clinical): Discovery Research OPERATIONS: QUALITY: Process development, Manufacturing & Production Quality Control & Assurance Discovery Research Process Development Director Supervisor & Process Development Technician Quality Control (QC) Bioinformatics Scientist Engineer Analyst Programmer Manufacturing & Production Supervisor Associate Technician (Operator) Instrumentation Tech Calibration Technician Facilities Management Manager Facilities Technician Shipper/receiver Chemistry Chemistry QC Analyst QC technician Microbiology Microbiology QC analyst QC Technician Quality Assurance (QA) Documentation Specialist QA Documentation Coordinator Clinical Research Clinical Research Manager Regulatory Affairs Manager Associate Data Manager Business Development Director of Business Development Administration Human resources Safety Manager •Careers in red indicate entry level positions All above require 2-4 year Entry level positions require an Assoc deg or certificate Higher entry levels require a BS, MS, PhD or Engineering degrees Can require medical, nursing or business degrees Senior Scientist Scientist III,II,I Research Associate CLINICAL RESEARCH: Clinical Research: Regulatory Affairs Clinical Research Clinical Research Manager Student Success Stories Students completing courses with certificate or Associate degrees in Biomanufacturing: www.biomanufacturing.org http://www.biomanufacturing.org/ 1. How to Start A Biotechnology Program (After getting support from the administration) Gain the support the Industry in your Area: – – – Find out the location and focus of each of the biotechnology/support companies within (10) miles of your school Understand the desired skills individuals (such as your students) should have (Most important of these are soft skills) Organize an advisory group that can assist you in curriculum building towards skills needed This will be a source of information as well as help with technical supplies 2. Find or Develop a Curriculum Resources High School Level-Entry Level Community College: Protein is Cash: Northeast Biotechnology Center and Collaborative , NBCC: www.biomanonline.org, Biomanufacturing.org Biotechnology: Science for the New Millennium: Ellyn Dougherty, EMC publisher, www.emcschool.com Basic Laboratory Methods in Biotechnology:Textbook and Laboratory Reference: Lisa Seidman et al, Prentice Hall, ISBN 013-795535-9 Align Curriculum with Program Goals What are your goals? – Two year associate degrees transfer to four year college – Two year associate degree and work – Certificate and immediate work Research and Development or Manufacturing? Goals can vary but should allow majority of your students to participate in. Four year college career pathway Biology Undergraduate Other Undergraduate or Engineer Biomedical Ph.D student Other Ph.D student Junior Postdoc & Senior Postdoc Industry Other Science Position Staff Scientist Assistant Professor Independent Investigator Intro to Biotechnology for High School/CC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Introduction to Biotechnology Use of bacteria, enzymes and fermentation by yeast Metrology Validation of Pipets and Calibration SOP ‘s & Documentation of Testing Basic Microbiology Basic Aseptic Technique and Testing of Unit 1 Bioload in Biomanufacturing Areas Gowning up Basic Microbiology Identify of Microbe Identification of Bacterial Types Morphology Unit 2 and Electrophoresis Transformation of Cells PGlO transformation of With DNA Bacteria Spectrophotometry Protein determination of samples By Bradford and UV analysis Genetic Transformation of Bacteria E. coli transformation with pGLO plasmid The Rain Forest:How do we find new Growth of pGlo transformed bacteria pharmaceuticals ? and isolation of the p-GLO product Proteins and their purification Isolation of casein from milk Using solubility and filtration techniques Good Manufacturing Practices GMP activity with popcorn Documentation And use of Documentation Chromatographic separation and how it Use of ion exchange and hydrophobic works columns in Isolating GFP QC Sampling of Product to Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Determine its Purity Biotechnology Curriculum 2. Associate Degree or Certificate Program Resources: Introduction to Biomanufacturing: Global Biomanufacturing Lab manual NBC2, at www.biomanufacturing.org Introduction to Biomanufacturing: Textbook, NBC2, at www.biomanufacturing.org Introduction to Biotechnology Lab Manual ATE central: Linnea Fletcher, et al ISBN BITC1311006 Techniques in Biotechnology Week Lecture and Topic Laboratory for Community College 1 Acids, Bases and Buffers Protein & Spectrophotometry Preparation of Buffers Determination of Protein in solution 2 Enzyme Kinetics Kinetics of LDH Protein structure Km of enzymes 3 Purification by pH Column Chromatography Precipitation of pro tein and Affinity chromatography 4 Enzyme Purification Purification of LDH by Ion Exchange using a IEX column 5 Identification of Proteins Concentration and Electrophoretic Techniques 6 High Pressure Chromatography Quality control Case study of Two Different Programs College Degree • Requirements will be more demanding in math, science • Comprehension, graphing &computer work is good can work independently • Has appropriate soft skills and can work well as a team member • Is good at trouble shooting problems in labs High School or Certificate • Entry level math is prealgebra or algebra 1 • Science background is sketchy (lacks chemistry) • Desire to be placed into a position after graduation • Likes science but needs reassurance • Needs to have SOP to carry out work High School Curriculum A Workshop to Instruct Teachers and Students in Biomanufacturing and the Bioeconomy Career Tracks: Protein is Cash Introduces Upstream Processing – Production of pGLO into protein by transformed cell Downstream Processing – Separation of cellular debris and cell supernatant – Purification of pGLO protein by Chromatography Quality Control – Identification of protein product by electrophoresis Discovery Research – How new drugs are discovered Biofuels 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Metrology Transformation of Bacteria Upstream Processing Downstream Processing Quantitative Analysis Discovery Research $Protein is Cash$ Local Teachers Workshops Biomanonline.org Day 1 : Metrology/Instrumentation Activities Outcomes • Calibration of top balance • Introduction of Good Manufacturing Practices • Verification of pipet performance • Pipetman Challenge • SOP and documentation • Confidence in measurements by instrumentation Metrology Day 2 Transformation of Bacteria Activities • Addition of pGLO plasmid to bacteria in Ca++ solution • Heat /shock the mixture • Plate cells onto selective Luria broth agar + ampicillin • Incubate overnight at 37oC • Note: arabinose acts to turn on the gene which starts production of pGLO protein Outcomes • Selection of cells by growing on ampicillin plates • Only transformed with cells will survive due to amp-r gene • Selected colonies will multiply in Luria broth at 37oC overnight • Aseptic technique and proper disposal of bacteria Day 2 E.coli Transformation with pGLO plasmid Ampicillin resistance gene (Ampr) and target gene on bacterial plasmid Cell division Bacterial clones Only E. coli containing plasmid survive on Ampicillin plates Transformation mixture is plated on to agar plate containing Ampicillin Results of Inserting Foreign DNA into an Organism Cells will multiply and produce desired gene product pGlO gene expression vector: Green Fluorescent Protein Day 2: Upstream Processing: Cell Growth and Lysis Activities • Transformed cells grown overnight in selected media are separated from media by centrifugation • Media is removed and packed cells are lysed • Homogenate is centrifuged • Supernatant with pGLO protein is retained for downstream processing Outcomes • Multiplication of cells • Initial separation of fluorescent protein from cell homogenate Day 3: Downstream Processing: Purification of Green Fluorescent Protein by Chromatography Activities • Separation of product by Different types of Chromatography – – – – Size exclusion Hydrophobic Interaction Cationic Interaction Anionic Interaction Outcomes • Fractions with green fluorescent protein will glow and be selected for analysis • Understand concept of chromatography as selective interactions of compounds with matrix Isolation and Purification of Green Fluorescent Protein Transformed cells Test tubes Fraction number #1 #2 #3 Courtesy of Bio-Rad Separation of Proteins by Column Chromatograph Separation by size – Size exclusion chromatography Separation by hydrophobic characteristics – Water loving vs water hating environments Separation by ionic charge – Protein has a positive charge & attaches to negative matrix on column: Cation Exchange – Protein has a negative charge & attaches to positive matrix on column: Anion Exchange Size Exclusion Chromatography Red molecule =10^6 daltons - Blue molecule = 600 daltons How Size Exclusion Works Molecular size of molecule will separate two or more molecules Large molecules can not go into a bead of a certain size and flows quickly through a column Small molecules enter into a bead and flows slowing through a column. Size of two different molecules are separated Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography H+ H+ H+ H+ Hi Salt High salt: Low salt 2M (NH4)2SO4 Wash buffer: 1.3 M (NH4)2SO4 Elution buffer: 10 mM Tris Ion Exchange Chromatography • Proteins bind to opposite charges on the matrix • An example of ion Exchange • Addition of increasing Salt/pH should release proteins Cation Exchange vs Anion exchange How proteins are attracted to ion exchangers Day 4: Quality Control Activities • Chromatography fractions prepared for electrophoresis • Electrophoresis Box is assembled with PAGE gel • Samples of chromatography fractions are added to PAGE gel and ran for 30 minutes • Gels stained and viewed Outcomes • Analysis of protein samples by observation on light box determines protein purity • Standard molecular weight markers indicate size of protein • Verification of mol wt by comparison with standard proteins and number of proteins in a single sample Quality Control Analysis of Column Fractions Isolated fractions using Ion Exchange Chromatography are then analyzed Electrophoresis by SDS PAGE of fractions collected Day 5. Discovery Research and FDA approval process Questions • Discovery Science in Drug development • Good Manufacturing Practices and the FDA • Initial Biomanufacturing Process Development • Scale up to full production of biologic /clinical trials Answers • Visit local biomanufacturing plants • Discuss importance of documentation in the workplace ie. SOP and Batch Records • Invite industry representatives to speak to the regulated workplace Bio-Rad Partnership Northeast Biomanufacturing Center and Collaborative (NBC2) is partnered with Bio-Rad: Provides teachers with engaging hands-on biomanufacturing education that is easily accessible Introduction to: – metrology, – production (upstream and downstream processing) – quality control biochemistry and clinical trials. These modules can be brought directly into the classroom Virtual Chromatography http://www.Atelearning.com/BioChrom HTTP Useful Information for Biomanufacturing http://www.Biomanufacturing.org http://www.Biomanonline.org http://www.Bio-link.org Background Resources: “Development of Biotechnology Curriculum for the Biomanufacturing Industry”, Robert McKown, and George L. Coffman, May/June 2002, Pharmaceutical Engineering pages 1-6. “ Introduction to Biomanufacturing a Global Biomanufacturing Curriculum” Northeast Biomanufacturing Center & Collaborative (NBC2) 2011, publisher :Lulu.com