* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of Populations
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
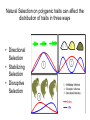
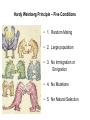
Evolution of Populations Gene Pool • All of the genes (including all of the alleles of those genes) that are in a population Relative Frequency • The number of times an allele occurs Evolution • (In genetics), evolution is anytime there is a change in the frequency in alleles in a population. Variation • Mutations = Mistakes or damage to DNA Sometimes effect phenotype but not always • Gene Shuffling= 23 pairs of chromosomes can produce 8.4 million combinations of genes Single / Polygenic • Single Gene Traits • A single gene has two alleles • Usually a dominant and recessive • Only two distinct phenotypes can be shown • Polygenic Traits • Often has two or more genes • Each gene has two or more alleles • Many possible genotypes and phenotypes Natural Selection on polygenic traits can affect the distribution of traits in three ways • Directional Selection • Stabilizing Selection • Disruptive Selection Directional Selection Disruptive Selection Stabilizing Selection Genetic Drift: in small populations an individual that carries a particular allele may leave more offspring than others and over time that trait may become more prevalent in the population Founder Effect • The new allele frequency is different from the original population Hardy Weinberg • Hardy Weinberg Principle states that the allele frequency in a population will remain at genetic equilibrium unless one or more factors cause it to change. If they do not change, the population will not evolve. Genetic Equilibrium • When allele frequencies in a population remain constant, Hardy Weinberg Principle – Five Conditions • 1. Random Mating • 2. Large population • 3. No Immigration or Emigration • 4. No Mutations • 5. No Natural Selection