* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MicroArray -- Data Analysis
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
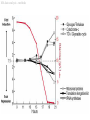
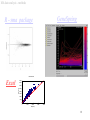
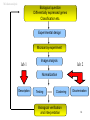
MicroArray -- Data Analysis Bioinformatics - 10p, October 2001 Cecilia Hansen & Dirk Repsilber 1 Overview • Bio-Informatic motivation • Monday – – – – MA experimental basic (C) MA data analysis (D) Introduction to lab 1 (C) lab 1 (C&D) • Tuesday – Introduction to lab 2 (D) – lab 2 (D&C) 2 Bio-Informatic motivation • Functional Genomics – adaptation and development – gene regulation & gene function – ”Transcriptome” (diagnostical purposes) • Analysis of large-scale noisy data – data management – statistical tools – associating further biological knowledge (database-links) 3 Overview • Bio-Informatic motivation • Monday – – – – MA experimental basic MA data analysis Introduction to lab 1 lab 1 • Tuesday – Introduction to lab 2 – lab 2 4 experimental basics Target (solid phase) 1) Genomic DNA or cDNA clones with known sequence. 2) PCR products are spotted on a glas slide in an organised way. 3) With a good printing device you can print at leased 10 000 spots (genes) on one microscope glas slide. 4) This gives you a matrix of spots, where every spot represents only ONE gene. ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** 5 experimental basics Probe control RNA is isolated from the cells t=0 • mRNA is a very instable molecule! t=0 t=1 sample t=2 t=3 ... t=7 • The amount of mRNA is in direct relation to the expression level of the gene. Make cDNA from mRNA with reverse transcriptase and incorporate fluorophores Cy3 and/or Cy5. 6 experimental basics Hybridization 1) Mix equal amounts ( 1:1 ) of Cy3 and Cy5 samples and hybridize it on to the array. green > red green = red green < red 2) The probe will bind to the complementary target to the array. 3) A laser scanner is then used to make the fluorophores to emit light with different wavelength. This will give us a picture of the array with spots in green, yellow and red. 7 MA data analysis • How do MA data look like ? • What are the specific questions ? • Methods 8 Overview • Bio-Informatic motivation • Monday – – – – MA experimental basic MA data analysis Introduction to lab 1 lab 1 • Tuesday – Introduction to lab 2 – lab 2 9 MA data analysis an expression profile like this for each gene : [mRNA] ~ Cy5/Cy3 = r 5_ 1 _ up-regulation induction down-regulation repression 0 Start of experiment time / h 10 MA data analysis Co-Regulation -- Inference function: expression: Differential • Which genes are differentially of Genes belonging expressed ? Comparing the to the same pathway are often Transcriptomes for two • Which genes are expressed in a showing the same regulatory different biological ”similar” way when comparing Expression-Fingerprinting: patterns (profiles) for a variety to expression profiles of genes samples (e.g. control, Often in medical applications of biological situations (or in a with known function? heat-shock) are it is of interestyou to characterize time series). (co-regulation) Reverse Engineering: the biological status of cells, interested in the subset of Hence, as a hypothesis, genes Using expression data to e.g. thewhich severeness of showing tumor of unknown function • patterns of expression genes are infer regulatory interactions cells, toregulatory be able to behaviour respond (diagnostic ”Fingerprinting”) similar expressed on different between a number of genes with the genes right therapy. as some of ”known” responsible for a certain levels • Reverse Engineering of function may have or a similar adaptation process genetic networks (up-/ down-regulated).11 function. developmental process. MA data analysis - methods 12 MA data analysis - methods GeneSpring R - sma_package Mean-Mean-Plot 40000 Excel 35000 Mean(Ch2) 30000 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 0 10000 20000 30000 40000 Mean(Ch1) 13 MA data analysis Biological question Differentially expressed genes Classification etc. Experimental design Microarray experiment lab 1 Image analysis lab 2 Normalization Description Testing Clustering Biological verification and interpretation Discrimination 14