* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
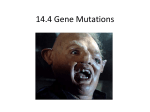
SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations d. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of new traits What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 1 LEQ#3: What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on DNA? What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 2 Vocabulary to Know: • • • • • Mutagenic Factor Mutation Mutagen Pesticides Herbicides • • • • • Radiation X-Rays/ UV rays Chemicals Viruses Phenotype What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 3 Mutagenic Factors • Agents in the environment that can change DNA are called mutagenic factors – Also called mutagens What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 4 Mutagenic Factors • Examples – UV rays in sunlight (Natural factor) – Radiation (X-rays and Nuclear) – Industrial Chemicals • Pesticides: Chemical substance used to against any pests. • Herbicides: Chemical substance used to kill plants • Cigarettes – Biological agent • Antimicrobial or disinfectant • Viruses What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 5 What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 6 Effects on DNA • Mutagenic factors can cause mutations – Change in the DNA that affects the sequence of nitrogen bases in the DNA • Changes that occur in the DNA sequence may or may not lead to changes in an organism What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 7 What is a mutation? • Change in an organisms DNA is called a mutation. • Not uncommon • May or may not affect the phenotype of an organism – Physical characteristics • May or may not have an impact of offspring What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 8 Effects on organism • Human body has DNA repair enzymes that help find and fix mutations • Although, sometimes these enzymes don’t work and the mutation is not fixed – The DNA site for the production of that enzyme has been damaged by the mutation • Errors or mutations can build up overtime and eventually effect how the cell works. – Mutations are a significant cause of aging What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 9 Explain how mutagens can cause genetic mutations in spite of your body’s DNA repair enzymes. What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 10 Answer • Mutagens may produce so much damage that the repair enzymes cannot keep up with the repairs. What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 11 LEQ#4: What are the types of alterations that can occur during replication? What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 12 Vocabulary to Know: • • • • Point mutation Framshift mutation Gene mutation Chromosomal mutation • Substitutions • • • • • • Deletion Duplication Inversion Translocation Nondisjunction Trisomy What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 13 Mutations • Two main types: – Gene Mutation • Mutation that causes a change in a single gene – Chromosomal Mutation • Mutation that involves the entire chromosome • Both can be caused by nature, random events, or environmental factors What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 14 Gene Mutations • Error in the sequence of nitrogen bases in a single gene – Remember: Codon (sequence of 3 nitrogen bases) corresponds to a particular amino acid • Two types of Gene Mutations: – Point mutation – Frame shift mutation What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 15 Gene Mutations • Error in the sequence of nitrogen bases in a single gene – Remember: Codon (sequence of 3 nitrogen bases) corresponds to a particular amino acid • Two types of Gene Mutations: – Point mutation – Frame shift mutation What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 16 Gene Mutation Point Mutation • Change in a single base is called a point mutation • Each of these words represents different amino acid. THE CAT ATE THE RAT • Now what would happen if you changed one letter? THE CAT ATE THE BAT • Still makes sense but the meaning is different – Effects are usually minimal if any at all • Example: Sickle Cell – GAG codon is changed to GTG – Inserts wrong amino acid What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 17 Gene Mutation Frameshift Mutation • Base is added/deleted is called a Frameshift mutation THE CAT ATE THE RAT Deleted one base: C THE ATA TET HER AT_ Added one base: C THE CCA TAT ETH ERA T • The statement makes no sense and the meaning is completely different – Effects much more severe than a point mutation – Codon for different amino acid What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 18 Wasting Syndrome • Gene mutation that results in the mutated form of myostatin protein. • Leads to overproduction of muscle tissue • Often seen in Belgian Blue and Piedmontese breeds of cattle What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 19 Explain why Frameshift mutations have a greater effect than do Point Mutations. What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 20 Answer • Point mutations typically affect only one codon (unless they create a premature stop codon). • A frame shift mutation affects all the codons in a gene that follow it. What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 21 Chromosomal Mutations • Changes in the number of chromosomes or their structure • Occur: Chromosomes fail to separate correctly during gamete production – Nondisjunction • Lead to abnormalities in offspring – Example: Cyclopia • 3 (trisomy) chromosomes of chromosome 13-15 or 17-18 What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 22 WARNING the following slide contains a disturbing image View at your own discretion What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 23 Cyclopia • Two eyes within one orbit • Proboscis-like appendage above the eye • Low-set or missing ears • Missing facial bones • Congenital heart disease • Do not survive What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 24 Chromosomal Mutations • 4 types of mutations – Deletion – Duplication – Inversion – Translocation What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 25 Chromosomal Mutation Deletion • Occurs when part of a chromosomes breaks off during mitosis/meiosis • Serious mutation that often causes death of the organism What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 26 Chromosome Mutation Duplication • Occurs when a section of a chromosomes is repeated • May cause genes to not function properly • Can also lead to developmental and physical disabilities What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 27 How could a mutated gene produce a shorter protein than that produced by the normal gene? What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 28 Answer A frame shift or a point mutation may have changed one of the codons to a stop codon What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 29 Chromosomal mutation Inversion • Occurs when a section of a chromosome breaks off, changes direction, and recombines to the same chromosome • Usually no serious effects • Genes are still intact and present on correct chromosome What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 30 Chromosomal Mutation Translocation • Piece of chromosome breaks off one chromosome and combines with a different chromosome • Causes serious physical and developmental disabilities What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 31 Translocation • Results in miscarriage of zygote usually • Produce gametes with wrong number of chromosomes • Usually harmless but can cause cancers (leukemia), and infertility What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 32 Did you know… • Mutations can occur in all types of organisms…even the human race. • One mutation that is very unlikely to be seen is multiple toes and fingers. • Doctors usually remove extra digits at birth. What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 33 LEQ#5: What relationships exist between mutations and the potential appearance of new traits? What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 34 Vocabulary to Know: • • • • • • • • Germ line mutation Somatic Mutation Sterile Inherited Meiosis Beneficial mutation Lethal Mutation Silent mutation • • • • • • • • Turners syndrome Down syndrome Klinefelters syndrome Cystic fibrosis Cancer Gametes Harmful mutation Intron What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 35 Consequences of Mutations • Depend on the type of cell the DNA mutation occurs in • Can occur in two types of cells – Somatic (body cell) – Germ line (gametes: sperm/egg) What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 36 Somatic Mutation • Are NOT passed down to offspring • Causes: – Random natural causes – Environmental factors: radiation, x-rays, sunlight – Chemical: cigarettes, cleaners, pesticides • Often lead to cancer What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 37 Germ Line Mutations • Mutations can be passed down to offspring (inherited) • Usually occur during Meiosis – Type of cell division the produces gametes in sexually reproducing organisms • Mutations in germ line affect the phenotype of the offspring. • Many are so severe that offspring do not develop properly and die before they can reproduce or are sterile – Incapable of producing offspring What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 38 Appearance of new traits • Impact on phenotype of organism – Silent mutation – Harmful mutation – Lethal mutation – Beneficial mutation • Impact on offspring What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 39 Impact on Phenotype • Many gene mutations do not affect an organisms phenotype. • Mutation that does not affect the resulting protein is called a silent mutation. • Mutation that occurs on the noncoding region (intron) may not affect the encoded protein at all. – Segment of gene that does not code for an amino acid What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 40 Impact on Phenotype • Chromosomal mutations affect a lot of genes and tend to have a big effect on an organism • Mutation that alters a important protein and affects its function is called a harmful mutation What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 41 Klinefelters Syndrome • • • • • • • • • • XXY (47 Chromosomes) Extra sex chromosome Sterile increase breast tissue, decrease in testosterone Greatly reduced male genitalia Some breast production Wide curvy hips No sperm production & no sex drive Sterile What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 42 Down Syndrome • Extra copy of chromosome 21 (47 chromosomes) • Broad short head • Malformed ears • Mental retardation • Protruding tongue when mouth is open • Impairment of cognitive and physical development What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 43 Turner’s syndrome • • • • • • • • • X0 ( 45 Chromosomes) only one female sex chromosome Short stature Wide-spaced underdeveloped nipples Webbed neck Swelling of hands & feet low hairline Sterile What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 44 Lethal Mutation • Mutations that lead to the death of an organism are considered to be lethal mutations What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 45 Patau’s Syndrome • Trisomy chromosomes 13-15 • Cleft lip and palate • Bone defects on skull • Large bulbous nose • Congenital heart disease • Majority die within a year What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 46 Edward’s Syndrome • Trisomy on chromosomes 17-18 • Small head • Ears deformed • Cleft palate • Severe retardation • Majority die within a year What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 47 Impact on the Phenotype • A very small percentage of all mutations actually have a positive effect these are called beneficial mutations. • These mutations lead to new versions of proteins that help an organism and its future generations better adapt to changes in their environment. • Example: – Deletion of CCR5 gene leads to HIV resistance – Found in European descent – Believe to be a result of survivors of the bubonic plague or small pox What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 48 Some genetic mutations are associated with increased risk for a particular disease. Tests exist for some of these genes. What might be the advantages and disadvantages of being tested What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 49 Answer • Advantage: – You would know what symptoms to look for – You would be able to prepare for treatment • Disadvantage: – There may be no cure for the disease – Simply having the gene may not mean that getting the disease is inevitable What are some mutagenic factors and what effects do they have on 50