* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex linked traits and autosomal diseases
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
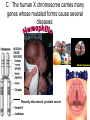
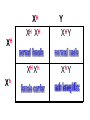
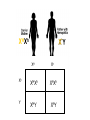
Sex-Linked Genes Review: Sex chromosomes determine sex II. Sex-linked traits A. First discovered by T. Morgan in fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) B. He figured out that the gene for white eyes was carried on the X chromosome C. The human X chromosome carries many genes whose mutated forms cause several diseases: Recently discovered, prostate cancer D. Human’s carry genes for color vision on the X chromosome. A Y chromosome is unable to cover up the defect What do you see? You should see a 26. Some will see a 2 & others a 6. Some people see nothing Can you trace a line from one "X" to the other? Someone with normal color vision will trace a orange/brown purple line and those with a slight deficiency will follow a different path. X X What do you see? Only colorblind people can see a 45 III. Sex-linked Punnett squares A. Hemophilia is carried on the X chromosome and is sex linked. B. Make a key: XHXH = normal female XHXh = female carrier XhXh = female with hemophilia XHY = normal male XhY = male with hemophilia Cross a normal male with a heterozygous female carrier. XHY XHXh H X h X XH XH XH Y XHY H h X X h X Y XHXh XHXh XH Xh Y Xh XHXh XH Xh Xh XHXh XhXh Y XHY XhY Gene Linkage • Thomas Hunt Morgan - worked with fruit flies – some traits appeared to be inherited together (gene linkage) – found that fruit flies have 4 pairs of chromosomes. • Each of the 4 groups of linked traits matched one of the chromosome pairs. – Concluded that chromosomes, not genes sort independently during meiosis. – Also concluded that due to crossing over, some chromosomes may exchange homologous genes during meiosis causing more diversity. Autosomal Recessive Diseases A. Caused by the inheritance of 2 recessive genes. 1. PKU (Phenylketonuria) – defect found on chromosome 12. Too much phenylalanine in body, lack of skin pigment, mental retardation (first one discovered) 2. Albinism – . 3 types - found on chromosomes 3, 9, or 15. no pigment in skin, hair and eyes 3. Cystic Fibrosis – Defect found on chromosome 7. Excess mucus in lungs. 4. Tay-Sachs – Defect found on chromosome 15, common in central and eastern european jews. Liquid accumulation in brain cells, mental problems, blindness, early death. Autosomal Dominant Diseases A. If a gene for the disease is inherited, the person inherits the disease 1. Achondroplasia – Dwarfism. Defect found on chromosome 4. 2. Hypercholesterolemia – too much cholesterol in blood. Defect on chromosome 13 3. Huntington’s Disease – Mental deterioration, uncontrollable movements, symptoms appear in middle age. Defect found on chromosome 4. V. CoDominant Diseases A. People who are heterozygous for blood cells inherit the disease 1. Sickle Cell Disease – an individual inherits a dominant gene for normal blood and a recessive defective gene (may also inherit 2 recessives to get disease). A defect in 1 base in the DNA is missing on chromosome 11 causes the body to makes glutamic acid instead of valine. Some red cells are made sickle shaped. Characteristics of Sickle Cell Disease • A common genetic disorder found in African Americans. – Red blood cells have a bent twisted shape – Their rigid shape causes them to get stuck in capillaries, and blood stops flowing damaging tissues and organs – Hemoglobin: a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells • In sickle cell disease hemoglobin is abnormal and the molecules stick together – When the body kills sickle cells it also kills the parasite that causes Malaria (benefit?) XII. Other Genetic Disorders • Cystic Fibrosis: most common among people with ancestors from northern Europe • Caused by a recessive allele on chromosome 7 • Serious digestive problems and thick heavy mucus that clogs lungs and breathing passageways • http://topdocumentaryfilms.com/treeman-searchfor-the-cure/ • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=renb0qQR7cA • http://health.discovery.com/videos/medicalmysteries-vod-treeman-disease.html