* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applying Mendel`s Principles Learning Objectives
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
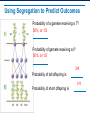
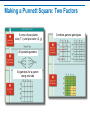
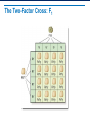
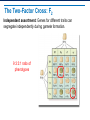
Applying Mendel’s Principles Learning Objectives Explain how geneticists use the principles of probability to make Punnett squares. Explain the principle of independent assortment. Explain how Mendel’s principles apply to all organisms. Determining Probability Probability: the likelihood an event will occur • Probability of either outcome: 50% or 1/2 • Three coin tosses? 1/2 × 1/2 × 1/2 = 1/8 • Each flip is an independent event. Using Segregation to Predict Outcomes Probability of a gamete receiving a T? 50%, or 1/2 Probability of gamete receiving a t? 50%, or 1/2 3/4 Probability of tall offspring is . 1/4 Probability of short offspring is . Genotype and Phenotype Genotype: genetic makeup Phenotype: physical traits Two organisms may share the same phenotype but have different genotypes . Heterozygous and Homozygous Homozygous: has two identical alleles for a gene Heterozygous: has two different alleles for a gene Which are: homozygous? 1, 4 heterozygous? 2, 3 1 2 3 4 Making a Punnett Square A cross of ospreys: beak size (B, b) Combine gamete genotypes Possible gametes Gametes for a parent along one side Making a Punnett Square: Two Factors A cross of pea plants: size (T, t) and pod color (G, g) All possible gametes All gametes for a parent along one side Combine gamete genotypes The Two-Factor Cross: F1 The Two-Factor Cross: F2 Independent assortment: Genes for different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation. 9:3:3:1 ratio of phenotypes Summary of Mendel’s Principles, Part I Inheritance is determined by units called genes passed from parents to offspring. , which are Where more than one form of a gene for a single trait exists, some alleles may be dominant and others recessive . Summary Mendel’s Principles, Part II • Each adult has two copies of each gene—one from each parent. These genes segregate from each other when gametes are formed. • Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently of each other.