* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular Biology Databases
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
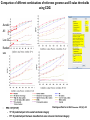
Investigation of factors affecting prediction of protein-protein interaction networks by phylogenetic profiling Anis Karimpour-Fard‡ , Ryan T. Gill† , and Lawrence Hunter‡ ‡ University of Colorado School of Medicine † Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, University of Colorado, Boulder [email protected] http://www.colorado.edu/che/research/faculty/gill/ http://compbio.uchsc.edu/Hunter Dec 1, 2007 The problem …… More than 500 Microbial genomes are fully sequence and there is high percent of genes with unknown function. For example: E. coli K12 15% P. aeruginosa 45% http://www.genomesonline.org/ X The meaning of protein function C B Z S A P D The function of protein A is its action on Substrate to form a Product Biochemical view Y A N M The function of A is the context of its interactions with other proteins in the cell Post genomic view Eisenberg, D. et. al. Nature 2000 Prediction protein function • Homology based methods (gives partial understanding about protein role) – Simple sequence similarity searches (BLAST) – Profile searches (PSI-BLAST) – Databases of conserved domains (Pfam, SMART) • Prediction from genomic context • • • • Phylogenetic profile Gene cluster Gene neighbor Rosetta Stone • Prediction from high-throughput experimental data – Microarray gene expression data – Protein-protein interaction screens – ... Phylogenetic Profile Pellegrini et al. PNAS 96, 4285 (1999) Marcotte et al. PNAS 97, 12115 (2000) 1- Select sets of genomes as a reference set Reference selection? Does the selection of the reference genomes influence the prediction? if so? How? 2- Create phylogenetic profile matrix for target organism: •Do one-against-all BLAST search to identify all homologous target genes in diverse reference organisms. Reference selection Measure profile similarities How E-value threshold effects the protein-protein interactions prediction? Blast E-value threshold (present or absent) Generate Protein-protein interactions network 3- Measure profile similarities Protein X: 110001111001001110001111 Protein Y: 111000111100000110001111 19 matching bits out of 24 4- Generate protein-protein interactions 2 nodes are connected if the 2 proteins have similar profile) Protein X 5- Create clusters from set of protein-protein interactions 6- Visualize network Protein Y Measure profile similarities Protein X 2 nodes are connected if the 2 proteins have similar profile) Protein Y Protein X: 110001111001001110001111 Protein Y: 111000111100000110001111 •Inverse homology •Calculate the homology between two genomes: • The ratio of number of homologs of each reference organism j to the number of proteins in the target genome i ( Hi,j) . •Pij =1/( Hi,j) otherwise Pij =0. Karimpour-Fard et al. BMC Genomics. 2007;8(1):393 •Pearson correlation coefficient •Mutual information MI(X,Y) = H(X) + H(Y) - H(X,Y) H(Y) = -∑p(i) ln p(i) p(i), (i= 0, 1) as the fraction of genomes in which protein Y in the state i 1 1 H(X, Y) p(i, j ) ln p(i, j ) i 0 j 0 Comparison of different combinations of reference genomes and E-value thresholds using COG Aerobic All Low GC Random sets • c) Karimpour-Fard et al. BMC Genomics. 2007;8(1):393 PPV =TP/(TP+FP) – TP = # predicted pair in the same functional category – FP= # predicted pair that were classified but were not same functional category Co-evolution can be used to assign function to unstudied genes Edge color code: • E. coli K12 (green) •E. coli O157 (blue) •Shigella flexneri (black) •S. typhimurium LT2 (purple) •P. aeruginosa (mustard) Hypothetical proteins YcgB,YeaH,YeaG are co-conserved across different species. Comparison of sub-graphs across species (CS-CCC) suggested that a previously unstudied S. typhimurium gene, ycgB, is functionally related to yeaH. Experimental data support the hypothesis that both genes are important for antimicrobial peptide resistance. Karimpour-Fard et al. Genome Biology 2007 8:R185