* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monohybrid Crosses - Life is a journey: Mr. T finding his way
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
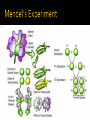
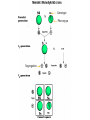
Natalia Sivackova Study Guide: pg. 26 Course Companion: pg. Pearson HL: pg. F1 generation had same characteristics of one of the parents F2 generation – characteristic that was lost in F1 reappeared in quarter of F2 Inheritance is based on factors that pass on from generation to generation Called genes Different forms of genes are called alleles Genes – factors that can be passed on from generation to generation Alleles – different forms of a gene F1 generation – the offspring of two parents F2 generation – the offspring of parents from F1 generation Homozygous – having two identical alleles of a gene (have same allele) Heterozygous – having two different alleles of a gene Dominant allele – an allele that has the same affect on the phenotype in a heterozygous individual as in a homozygous individual Recessive allele – an allele that only has an effect on the phenotype in homozygous individuals. In heterozygous individuals the recessive allele is hidden by the dominant allele Genotype – the alleles possesed by an organism (e.g. Ss) Phenotype – the characteristics of an organism (e.g. smooth seed) Punnett squares – used to show all the possible outcomes of a cross Segregation – the seperation of two alleles Genotype Phenotype Segregation http://www.scq.ubc.ca/a-monks-flourishinggarden-the-basics-of-molecular-biologyexplained/ http://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucbhjow/royal_free/m odel_answer_1998.html