* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Timing and Development of Growth
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
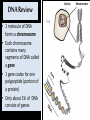
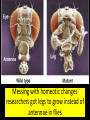
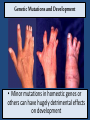
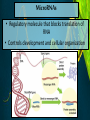
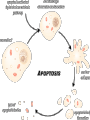
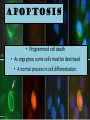
Timing and Development of Growth Big Idea 2E: Many bio processes involved in growth, reproduction, and homeostasis include temporal regulation and coordination Essential Knowledge • 2E1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. • 2E2: Timing and coordination of physiological events are regulated by multiple mechanisms. All Cells in an Organism Contain Same DNA • Came from same zygote dividing over and over again DNA Review • 1 molecule of DNA forms a chromosome • Each chromosome contains many segments of DNA called a gene • 1 gene codes for one polypeptide (portion of a protein) • Only about 1% of DNA consists of genes Gene Expression • DNA in nucleus is transcribed into RNA • RNA exits nucleus and is translated into a polypeptide by ribosomes Control of Transcription • Enzyme that transcribes DNA (RNA Polymerase) requires transcription factors • Activation of transcription factors triggers transcription, thus expressing the gene. Cells Are Different Because they Express Different Genes • Each cell generates different proteins and at different times • Very complicated, focus of research currently During Development Different Genes Are Expressed • Homeotic genes control developmental patterns and sequences Determine where each body part develops Messing with homeotic changes researchers got legs to grow instead of antennae in flies Embryonic Induction • As cells develop and mature, they cause other cells to express certain genes • Ex: as eye forms, one cell causes others to express genes necessary to make eye cells • Allows each cell to develop at correct time For Plants… • Temp and water availability determine seed germination and embryo growth. All Cells Originally Can Be Anything! • But over time processes (DNA methylation/ induction) restrict what genes are expressed • When new cells form they usually have same genes shut off as parent cell DNA methylation shuts off many genes!! Genetic Mutations and Development • Minor mutations in homeotic genes or others can have hugely detrimental effects on development MicroRNAs • Regulatory molecule that blocks translation of RNA • Controls development and cellular organization Apoptosis • Programmed cell death • As orgs grow, some cells must be destroyed • A normal process in cell differentiation. Originally there are cells between your fingersthey die, separating the fingers