* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
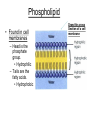
Organic Compounds • Contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. • Carbon is found in things that are or once were living. • Carbon atoms share electrons to form covalent bonds. Organic Compounds • Organic compounds are composed of hundreds to thousands of individual molecules. – The single molecules in a polymer are called monomers. Organic Compounds • The long molecules formed by repeating patterns of monomers are called polymers. Macromolecules • 4 Types of Organic Compounds or macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. – Essential to maintaining life processes: cell function, storage, energy, homeostasis and genetic information. Carbohydrates • Make up sugars and starches, fiber • Contain atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • The ratio of the atoms is 1 C : 2 H : 1 O • Provide energy to the cells. • Dissolve in water (hydrophilic) Lipids • The three types of lipids are fats, oils, and waxes. • Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Functions of Lipids • Lipids store energy for later use by the body. • Lipids also serve as padding and protection for the body. • Lipids are composed of C, H, and O molecules, but the molecules are more complex than carbohydrates. Phospholipid • Found in cell membranes – Head is the phosphate group. • Hydrophilic – Tails are the fatty acids. • Hydrophobic Draw this cross Section of a cell membrane Proteins • Proteins are the building materials for the body. – Hair, skin, muscles, and organs are made mostly of proteins. • Composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen Function of Proteins • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids (monomers). • Serve as enzymes which control rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. . Nucleic Acids • DNA and RNA molecules • Made of C, H, O, N, P, S elements • Very large molecules that determines the genetic traits Made up of smaller units called nucleotides