* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
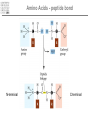
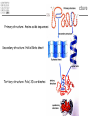
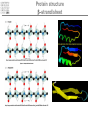
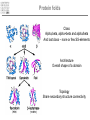
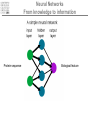
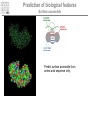
It & Health 2010 Summary Thomas Nordahl Petersen DNA/RNA • • • • • • • • • DNA findes I celle kernen (Eukaryoter) base paring T substituted with U in RNA Reading direction Reading frame (1,2,3,-1,-2,-3) 64 codons DNA -> mRNA Intron, exon & UTR (non-coding exon) Intron/Exon splice site Reading frame and reverse complement Having a piece of DNA like: TGCCATGCATAGCCCCTGCCATATCT Forward strings & reading frames 1 : TGCCATGCATAGCCCCTGCCATATCT 2 : GCCATGCATAGCCCCTGCCATATCT 3 : CCATGCATAGCCCCTGCCATATCT Reverse complement strings & reading frames -1: TCTATACCGTCCCCGATACGTACCGT -2: CTATACCGTCCCCGATACGTACCGT -3: TATACCGTCCCCGATACGTACCGT Amino acids 20 naturally occurring amino acids - mRNA -> protein Reading direction 4 backbone atoms Amino acid properties - - Acidic, basic, polar, charged, hydrophibic 1 and 3 letter codes Amino Acids Amine and carboxyl groups. Sidechain ‘R’ is attached to C-alpha carbon The amino acids found in Living organisms are L-amino acids Amino Acids - peptide bond N-terminal C-terminal Databases and web-tools Databases and biological information • Genbank • Uniprot Web-tools • NCBI Blast • UCSC genome browser • Weblogo CENTER FOR BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE ANALYSIS Theory of evolution Charles Darwin 1809-1882 Phylogenetic tree Global versus local alignments Global alignment: align full length of both sequences. “Needleman-Wunsch” algorithm). (The Global alignment Local alignment: find best partial alignment of two sequences (the “Smith-Waterman” algorithm). Seq 1 Local alignment Seq 2 Pairwise alignment: the solution ”Dynamic programming” (the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm) Sequence alignment - Blast Sequence alignment - Blast Blosum & PAM matrices • Blosum matrices are the most commonly used substitution matrices. • Blosum50, Blosum62, blosum80 • PAM - Percent Accepted Mutations • PAM-0 is the identity matrix. • PAM-1 diagonal small deviations from 1, offdiag has small deviations from 0 • PAM-250 is PAM-1 multiplied by itself 250 times. Sequence profiles (1J2J.B) >1J2J.B mol:aa PROTEIN TRANSPORT NVIFEDEEKSKMLARLLKSSHPEDLRAANKLIKEMVQEDQKRMEK Log-odds scores • BLOSUM is a log-likelihood matrix: • Likelihood of observing j given you have i is – P(j|i) = Pij/Pi • The prior likelihood of observing j is – Qj , which is simply the frequency • The log-likelihood score is – Sij = 2log2(P(j|i)/log(Qj) = 2log2(Pij/(QiQj)) – Where, Log2(x)=logn(x)/logn(2) – S has been normalized to half bits, therefore the factor 2 BLAST Exercise Genome browsers - UCSC Intron - Exon structure Single Nucleotide polymorphism - SNP SNPs Protein 3D-structure Protein structure Primary structure: Amino acids sequences Secondary structure: Helix/Beta sheet Tertiary structure: Fold, 3D cordinates Protein structure -helix helix -helix Pi-helix 3 residues/turn - few, but not uncommon 3.6 residues/turn - by far the most common helix 4.1 residues/turn - very rare Protein structure strand/sheet Protein folds Class Alpha,beta, alpha+beta and alpha/beta And last class – none or few SS-elements Architecture Overall shape of a domain Topology Share secondary structure connectivity Protein 3D-structure Neural Networks From knowledge to information Protein sequence Biological feature Use of artificial neural networks • A data-driven method to predict a feature, given a set of training data • In biology input features could be amino acid sequence or nucleotides • Secondary structure prediction • Signal peptide prediction • Surface accessibility • Propeptide prediction C N Signal peptide Propeptide Mature/active protein Prediction of biological features Surface accessible Predict surface accessible from amino acid sequence only. Logo plots Information content, how is it calculated - what does it mean. Logo plots - Information Content Calculate Information Content I = a palog2pa + log2(4), Maximal value is 2 bits Sequence-logo Completely conserved ~0.5 each • Total height at a position is the ‘Information Content’ measured in bits. • Height of letter is the proportional to the frequency of that letter. • A Logo plot is a visualization of a mutiple alignment.