* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BENCHMARK #2: Cell Division and Genetics
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
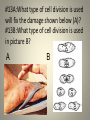
BENCHMARK #2: Cell Division and Genetics #1A: Name the major steps in the process shown below? 1B: Name an organism that uses this as a means of reproduction. 1C: During which phase does replication occur? #2A: What two processes are illustrated in the diagram below? #2B: What would be the RNA sequence to the following: TCT-AGA? #3A: Why are the following most easily seen during mitosis (not Interphase)? #3B: What gender is this person? #3C: What are chromosome displays like this called? #4A: What process is being shown in the diagram below? #4B: During what type of cell division does this occur? #4C: What advantage does this have to the species? #5A: What type of genetic pattern of inheritance is responsible for the diversity of skin colors seen in humans? #5B: What would a graph of these genotypes look like? #6A: What amino acid is coded for by the DNA sequence CCC? #6B: What are groups of three nucleotides called? #7A: What pattern of genetic inheritance is color-blindness? #7B: Why can’t males be a carrier for this trait? #7C: Which gender suffers from these types of traits the most often? #8A: During transcription what type of molecules separates the chains of DNA? #8B: What type of bond holds the chain together? #8C: Between what two molecules does the enzyme cut? 8d: What process occurs in the nucleus? In the cytoplasm? #9A: What appears to be the cause of the difference in the growth of wings in the flies shown below? #9B: Give an example of a similar effect in humans. Grown above 25 degrees C Grown below 25 degrees C #10A: What happens during the G1 phase? G2? #10B: What is being synthesized during the S phase? #10C: What occurs during the M Phase? A #11: Identify each stage of mitosis below. When does replication occur? C B D #12A: What type of mutation is shown below? #12B: What are the “Big Three” causes of mutation? #13A:What type of cell division is used will fix the damage shown below (A)? #13B:What type of cell division is used in picture B? A B #14A:What type of cross is this that allows you to determine the genotype of plant A? A #15:What type of genetic pattern is demonstrated by human blood types? #15B: Explain how a man with blood type A and a women with type B can have a child with blood type O. #16A: Why is the zygote diploid? #16B: What type of cell division created the egg and sperm (gametes)? #17A: How is it possible for two normal parents to produced an affected child? #17B: How is the genetic information transmitted to MMMMMMM the child? #18A: Give an example of a human genetic disorder that is autosomal dominant (like the one below). #18B: What are the genotypes of the parents in the first generation? #19: Why do your cells, which are genetically identical, appear different? Muscle Cheek Cells Red Blood Cells #20A: How many males are in the following pedigree? Generations? #20B: From whom does person #12 get the disorder? 2 #20C: How are person #2 and #12 related? 12 #21A: What type of RNA is shown below? #22B:What role does it bbbbb play in protein synthesis? #22A: What process is being shown below? How many chromosomes do the end cells have? #22B:Why must sexually reproducing organisms go through this process? #23A: What segment would be the complementary to the following strand of DNA? #23B: What process is used to create the new strand? • ___________________________________ •C C G A T A G C G #24A: The pedigree below shows what type of genetic cross (pattern)? #24B: What is true about this type of cross (pattern) concerning gender? #25: Two heterozygous tall plants are crossed. What are the expected percentages of tall and short plants in the F1? #28: Huntington’s Disease is an autosomal dominant disorder. A man marries a woman without the disease. They have a child without the disease. How is this possible? #28: If 20% of nucleotides in a sample of DNA have the base Thymine, what percentage of the nucleotides contain Cytosine, Adenine, and Guinine?