* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration - Local.brookings.k12.sd.us
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
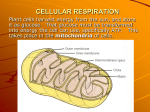
http://www.clickatutor.com/mitochondria.jpg Cellular Respiration Campbell Chapter 9 Slide shows modified from: Glenbrook High School AP site http://gbs.glenbrook.k12.il.us/Academics/gbssci/bio/apbio/Index/index.htm & Dr. Chuck Downing http://gohs.tvusd.k12.ca.us/TeacherWebs/Science/CDowning/default.aspx http://www.inclusive.co.uk/downloads/images/pics2/tree.gif ___________ use energy from sunlight or chemicals to make their own food In the last chapter green plants used ________________ trap energy from __________ and make ______________ http://206.173.89.42/REALTYWITHALOHA_COM/piphoto/funny%20sun%20with%20sunglasses.gif In this chapter, we will learn how this glucose is ____________ by organisms and the _______ is stored as _______ What kind of organisms do this? ALL LIVING THINGS NEED ENERGY! All organisms burn glucose for fuel plants fungi Animals (Including humans) bacteria PHOTOSYNTHESIS ___________ + _________ + ___________ →_______________ + __________ CELLULAR RESPIRATION _____________ + _________ →________ + __________ + __________ ______________________________________________________________ http://www1.istockphoto.com/file_thumbview_approve/777814/2/istockphoto_777814_oil_bonus_pack.jpg REMEMBER: ______________ OXIDATION Is Loss of electrons Remove H Releases energy Exergonic REDUCTION Is Gain of electrons Add H Stores energy Endergonic Loss of hydrogen atoms Energy Gain of hydrogen atoms CELLULAR RESPIRATION happens __________ in ________________. If all the energy was released in one step… most would be lost as ____________________! See why cells use cellular respiration http://plato.acadiau.ca/COURSES/comm/g5/Fire_Animation.gif ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN • Prevents energy release in 1 explosive step • Allows energy to be released slowly in steps and captured as ATP • Electron route: food → NADH → ETC → oxygen MITOCHONDRIA = cell power plant Surrounded by ___________ membrane Outer membrane & Inner membrane (called _______________ ) Space between inner membrane & outer membrane = ____________________ Space inside cristae folds = _________________ HIGH ENERGY ELECTRON CARRIERS FAD → FADH2 NAD+ → NADH The first step in cellular respiration = _______________ Also called _________________________________ • happens in the ________________ outside the mitochondria • occurs _________________________ See glycolysis movie • Details of glycolysis Steps 1 – 3 A fuel molecule is energized, using ATP. Glucose Step PREPARATORY PHASE (energy investment) 1 Glucose-6-phosphate 2 Fructose-6-phosphate 3 Fructose-1,6-diphosphate Step 4 A six-carbon intermediate splits into two three-carbon intermediates. 4 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) ENERGY PAYOFF PHASE 5 Step 5 A redox reaction generates NADH. 6 Steps 6 – 9 ATP and pyruvic acid are produced. 1,3-Diphosphoglyceric acid (2 molecules) 7 3-Phosphoglyceric acid (2 molecules) 8 2-Phosphoglyceric acid (2 molecules) 2-Phosphoenolpyruvate (2 molecules) 9 Pyruvic acid (2 molecules per glucose molecule) Glycolysis (GLYKOS = ________ LYSIS= ___________ ) Requires ____________to get it started. ____________________________________ = using energy from breaking a chemical bond to add MITOCHONDRION aP directly from a phosphorylated molecule to ADP without a proton gradient PYRUVIC ACID MOVES TO NEXT STEP IF THERE IS NO OXYGEN (______________) IF THERE IS OXYGEN (_____________) Cellular respiration •Glycolysis: cytosol; glucose → pyruvate •Kreb’s Cycle: •mitochondrial matrix; •pyruvate → CO2 •NADH made Electron Transport Chain: cristae; NADH & FADH2 donate electrons → oxygen Pyruvate is transported into mitochondrion and Acetyl CoA produced For each pyruvate converted into acetyl CoA 1 molecule of CO2 is released; NAD+ ---> NADH; Krebs Cycle AnimationCoenzyme A (from B vitamin) Kreb’s Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle Animation Kreb’s Cycle • Oxaloacetate (OAA) combines with 2 C’s from Acetyl CoA to make Citric acid • CoA recycles • 2 C atoms from pyruvate → exit as CO2 For each pyruvate that enters: 2 CO2 released 3 NAD+ reduced to 3 NADH; 1 FAD+ reduced to 1 FADH2 (riboflavin, B vitamin); 1 ATP molecule Electron transport chain NADH More on Making ATP FADH2 • 3 places in the chain make ATP • Electrons from NADH start “higher” in the waterfall, so they generate more ATP than FADH2 electrons, which start “lower” in the waterfall and miss one ATP-generating step. Electron transport chain • ETC includes Cytochromes Ubiquinone (Q) • NADH & FADH2 pass electrons pass down ETC • Energy from moving electrons concentrates H+ ions in __________________ • ________________: harnesses the flow of H+ back into the matrix make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation) • ________ is final electron acceptor → ________ Cellular Respiration Grand Total • Glycolysis: →2 ATP (substrate-level phosphorylation) • Kreb’s Cycle:→ 2 ATP (substrate-level phosphorylation) • Electron transport & oxidative phosphorylation: 2 NADH (glycolysis) → 6ATP 2 NADH (acetyl CoA) →6ATP 6 NADH (Kreb’s) → 18 ATP 2 FADH2 (Kreb’s) → 4 ATP 38 TOTAL ATP from 1 molecule of glucose (-2 ATP to transport 2 pyruvate into mitochondria) NET of 36 ATP WHAT IF THERE IS NO OXYGEN? = ANAEROBIC IF THERE IS NO OXYGEN (______________) IF THERE IS OXYGEN (_____________) = AEROBIC Related metabolic processes Fermentation: • alcohol~ pyruvate →ethanol • lactic acid~ pyruvate → lactate ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION _______ +_____ →__________ + ______ + _____ • Happens when yeast makes bread dough rise • CO2 bubbles make air spaces in bread • Alcohol evaporates during cooking http://www.deliciousdelicious.com/archives/herb%20bread%201.jpg ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION _______ +_____ →__________ + ______ + _____ Used to make alcoholic beverages http://www.firstpath.com/images/alcohol.jpg LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION _______ +_____ →______________ + ________ Happens in muscles during exercise when body can’t get oxygen to tissues fast enough. Lactic acid builds up in muscles causing soreness http://www.miranda.com/library.en/Images/Pictures/girls-runners.jpg LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION _______ +_____ →______________ + ________ Happens when bacteria are used to make foods and beverages like yogurt, cheese, buttermilk, sauerkraut, kimchi http://chronicle.augusta.com/images/headlines/032200/DANNON_YOGURT.jpg http://www.reillydairy.com/natural_cheese.html WHY DO FERMENTATION? WHY NOT JUST KEEP MAKING ATP USING GLYCOLYSIS? WITHOUT OXYGEN, PYRUVIC ACID ___________ and all the _______ carriers get full. Eventually glycolysis will NAD+ PYRUVIC ACID +_____ _______ CO2 + _____ →ALCOHOL __________ + ______ LACTIC ACID ______ You get the NAD+ carriers back FERMENTATION HAPPENS so cells can ____________________ needed to keep glycolysis going __________________________ = organisms that can make ATP using either fermentation or cellular respiration Ex: yeast and many bacteria With oxygen pyruvate → Krebs cycle Without oxygen → fermentation Organisms can use a variety of molecules for fuel __________________= breakdown of fatty acids into 2 carbon fragments that enter Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA 1 g of fat → twice as much ATP as 1 g of carbohydrate Evolutionary Significance • Most widespread metabolic pathway… suggests ancient prokaryotes probably used glycolysis to make ATP before oxygen was present • Earliest fossil bacteria present 3.5 billion years ago but large amounts of oxygen not present until 2.7 billion years ago • Glycolysis happens in cytoplasm without membrane bound organelles suggests it was found in early prokaryotic cells since eukaryotes appeared 1 billion years after prokaryotes (Endosymbiotic theory) VOCAB OVERLOAD ? __________________________ = Generation of ATP from a proton gradient. It occurs in all living things Chloroplasts do it to make ATP in light reactions Mitochondria do it to make ATP following ETC http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/energy/atpsynthase_il.html Prokaryotes create gradient across cell membrane to make ATP to pump nutrients & waste and move flagella _________________________ = Using hydrogen gradient generated by thylakoid membrane during the light reactions of photosynthesis to make ATP CHLOROPLAST _________________________________ = using proton gradient created by electron transport chain in cristae membrane to make ATP MITOCHONDRION ______________________________________ = using energy from breaking a chemical bond to add MITOCHONDRION aP directly from a phosphorylated molecule to ADP without a proton gradient