* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanism of ribonuclease
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
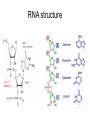
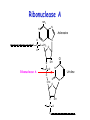
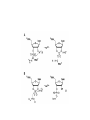
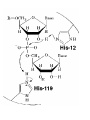
Mechanism of ribonuclease RNA structure Structure Of RNase protein • The size of RNase A is small: • Has 124 amino acid residues • Contains 19 of the 20 natural amino acids, lacking only tryptophan • Has similar shape to a kidney with active site residues lying in the cleft Structure Of RNase protein • Long four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet and three short α-helixes • Cross-linked by four disulfide bonds involving all eight of its cysteine residues Example of acid-base catalysis: • Ribonucleases are enzymes that hydrolyze RNA by cutting the P-O ester bond attached to ribose 5’ carbon. • It represents a typical example of acid base catalysis. Ribonuclease A NH2 N N O O P Adenosine N N O CH2 O O O Ribonuclease A O O OH N P O Uridine O O CH2 O O P O N O OH O RNA Binding SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY: • RNase A catalyzes the cleavage of the PO bond of an RNA strand and the hydrolysis of the P-O bond of a nucleoside 2’,3’-cyclic phosphodiester on the 3’-side of a pyrimidine residue. • Pancreatic RNase is specific for a pyrimidine base (uracil or cytosine) on the 3’ side of phosphate bond that is cleaved. • The hydrolysis of RNA catalyzed by RNase A occurs in two steps with a 2’,3’ cyclic phosphate diester intermediate. Mechanism of RNase A Figure 11-10 part 1 Mechanism of RNase A Figure 11-10 part 2 In the formation of 2’,3’ cyclic phosphate diester intermediate. • His 12 acts as general base and remove the proton from 2‘-hydroxy group of ribose. • This will increase the nucleophilic character of the oxygen atom. • His 119 will act as general acid and protonate one oxygen of the phosphate –ve charge. • The side chain of Lys41 and the main chain of Phe120 enhance catalysis by stabilizing this transition state