* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Production of Turnip yellow mosaic virus Capsids: The Future in
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
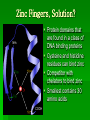
Production of Turnip yellow mosaic virus Capsids: The Future in Micronutrient Delivery Nicole Dzialowy Dr. Yannis Tzanetakis Dr. Theo Dreher Department of Microbiology Zinc Deficiency Diets rich in grains and low in protein suffer in zinc Many developing countries Importance of Zinc Plays critical role in cell growth and division Required for protein and DNA synthesis Zinc plays a role in immune system Concerns: Increased risk of common infections and growth stunting in children Women who are pregnant or lactating Shortages of Zinc Phytate Lost availability due to interactions with other components of diet Zn interacts with chelators derived from grains and legumes zinc Unavailable to be absorbed after binding to chelator Phytate Zinc Fingers, Solution? Protein domains that are found in a class of DNA binding proteins Cysteine and histidine residues can bind zinc Competitor with chelators to bind zinc Smallest contains 30 amino acids NH2 COOH Project Outline To develop protein nanospheres as a protective and nutritious delivery vehicle for zinc Nanosphere = Turnip yellow mosaic virus My Summer Project To produce TYMV virions in Escherichia coli, using a recombinant vector that includes the capsid protein sequence E.coli Strategy Food-grade Lactobacillus Zinc Fingers Nanosphere: Turnip yellow mosaic virus Turnip yellow mosaic virus (TYMV) Background Positive strand RNA virus Structure 28 nanometer spherical virion (capsid) Capsid built of 180 copies of the same protein Capsid is stable in the absence of genome Atomic structure is known Protein Structure of TYMV Amino acid sequence for coat protein is known Green and red arrows mark possible regions for zinc finger insertion Both regions face interior of capsid Methods 1. Isolate/purify pET 11d 2. Amplify CP RNA with RT-PCR 5’ Coat protein NcoI 3’ BamHI 3. Restriction digest with NcoI and BamHI pET 11d 4. Ligate pET 11d and CP insert 5’ 3’ 5’ Coat protein pET 11d NcoI Coat protein 3’ BamHI Methods (cont’d) 5. Transform into DH5α E.coli cells and isolate plasmid 6. Restriction mapping and sequencing CP insert pET 11d DH5α cells 8. Extract/purify capsid and observe by electron microscope 7. Transform into BL21 (DE3)-RP E.coli cells pET 11d BL21 cells T7 RNA Polymerase Results 1 2 3 4 5 6 bp 5000 1500 1000 750 500 250 1 % TBE agarose gel (Gene Ruler 1kb ladder) Sequence of CP insert Western blot analysis results Some minor expression, but not as expected Future Work Extract/purify capsid, observe on electron microscope Engineer TYMV capsids with zinc fingers in order to bind zinc Explore production of zinc-loaded TYMV capsid in food-grade Lactobacillus lactis Acknowledgements Howard Hughes Medical Institute Dr. Kevin Ahern Dr. Yannis Tzanetakis Dr. Theo Dreher Dreher Laboratory Dr. Dave Williams Laboratory