* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vitamins in metabolism
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
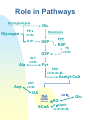
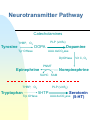
Vitamins and Vitamin-Like Substances •Names and roles - vitamins •Names and roles - vitamin-like •Deficiencies and sources -vitamins •Deficiencies and sources - vitamin-like •Role in pathways •Neurotransmitter overview •Neurotransmitter pathway •Tetrahydrofolate conversions •Tetrahydrofolate examples •B12 pathways Eric Niederhoffer SIU-SOM Names and Roles Vitamins A retinol phototransduction B1 thiamine carbohydrate metabolism B2 riboflavin redox, respiration B3 niacin redox B5 Pantothenic acid B6 tca, fa and cholesterol pyridoxine pyridoxamine pyridoxal aa metabolism glycogenolysis B7 Biotin gluconeogenesis, tca, fa, aa B9 Folic acid 1C metabolism B12 cobalamin 1C&H metabolism C ascorbic acid hydroxylation D cholecalciferol bone remodeling E tocopherols antioxidant K phytylmenaquinone multiprenylmenaquinone coagulation bone remodeling Names and Roles Vitamin-Like Substances Choline ac, pl Carnitine fa acyl group transfer Bioflavonoids antioxidants Lipoic acid tca acyl group transfer Coenzyme Q electron transport Inositol phospholipids p-Aminobenzoic acid folate component Deficiencies and Sources Vitamins preformed: liver, egg yolk, butter, milk b-carotene: dark green and yellow veggies A - night blindness B1 - beri-beri B2 - pellagra seeds, nuts, wheatgerms, legumes, lean meat B3 - pellagra meats, nuts, legumes meats, nuts, legumes B5 - none known yeast, grains, egg yolk, liver yeast, liver, wheatgerm, nuts, beans, bananas corn, soy, egg yolk, liver, kidney, tomatoes B6 - neurologic disease B7 - widespread injury B9 - anemia yeast, liver, leafy veggies B12 - pernicious anemia liver, kidney, egg, cheese C - scurvy citrus and soft fruits D - ricketts, osteomalacia E - neurologic?, hemolytic anemia K - bleeding disorders milk, fortified food, fish oils, egg yolks, liver veggie oils, nuts green leafy veggies, fruits, dairy products, veggie oils, cereals, meats Deficiencies and Sources Vitamins-Like Substances Choline - rare whole eggs, liver, beef steak, and soy (lecithin) Carnitine - unlikely meat, dairy products, asparagus, wheat grem Bioflavonoids - none known Lipoic acid - none known Coenzyme Q - rare Inositol - none known p-Aminobenzoic acid - see B9 fruits, vegetables, tea, coffee, cocoa, wine, beer liver fruits, vegetables, meats cereal grains liver, rice bran, whole wheat Role in Pathways Glycogenolysis Glycogen Glc PP a vit B6 G1P Glycolysis G6P PPP R5P TK vit B1 G3P Ala ALT vit B6 Pyr PDH vit B1,B2,B3 Acetyl-CoA Asp AST vit B6 OA TCA cycle SCoA vit B6 aKG aKGDH vit B1,B2,B3 Glu Neurotransmitter Overview PLP (vit B6) g-Aminobutyrate Glutamate deCO2ase PLP (vit B6) Tyrosine Dopamine Norepinephrine deCO2ase Epinephrine PLP (vit B6) Tryptophan Serotonin deCO2ase Neurotransmitter Pathway Catecholamines PLP (vit B6) THBP, O2 DOPA Tyrosine Dopamine AAA deCO2ase Tyr OHase DbOHase Vit C, O2 PNMT Epinephrine Norepinephrine SAHC SAM THBP, O2 PLP (vit B6) 5HTP Tryptophan Trp OHase Serotonin AAA deCO2ase (5-HT) Tetrahydrofolate Conversions Folate DHF reductase (dUMP to dTMP to DNA) DHF DHF reductase THF Most oxidized (Ser to Gly) (HC to Met) (His to Glu) N10-formyl-THF N5-formimino-THF N5,N10-methenyl-THF N5,N10-methylene-THF N5-methyl-THF Most reduced Tetrahydrofolate examples NAD+ THF PLP N5,N10MLTHF THF Ser NADH + H+ N5,N10MLTHF CO2 + NH4+ Gly serine hydroxymethyl transferase glycine synthase N5-FTHF THF His Glu glutamate formimino transferase dUMP dTMP thymidylate synthase N5,N10MLTHF A series of reductases 7,8-DHF THF DHF reductase B12 Pathways Odd-chain FA oxidation/ AA metabolism MMCoA mutase L-MMCoA SCoA Vit B12 (H exchange) TCA cycle Methyl transfers (1C metabolism) Met Ad transferase ATP + Met S-AdMet THF R Met synthase Vit B12 N5MTHF A variety of MTs R-CH3 hydrolase HC Purines, dTMP S-AdHC Review Questions What are the different names for vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, and B12? Which pathway depends on vitamin A? Which pathways and enzymes depend on vitamin B1, B2, B3, B6 and B12? Which pathway and enzyme depends on choline? Which pathways and enzymes depend on folic acid?