* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cellular transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
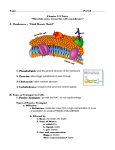
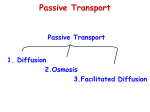
CELLULAR TRANSPORT SBI 3C SEPTEMBER 2010 PASSIVE TRANSPORT: Transport that does not require energy. Important Terms: Dynamic equilibrium: A state of balance where particles move in all directions at equal rates. Selectively Permeable: Allows only certain substances to pass through it. Concentration gradient: A difference in concentration between two areas Transmembrane Protein: A protein molecule in a membrane that spans the thickness of the phospholipid bilayer (goes all the way across the membrane) Carrier Protein: A transmembrane protein that facilitates the diffusion of certain substances through the membrane. SIMPLE DIFFUSION A movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration Process continues until dynamic equilibrium is reached and particles are spread out evenly Examples: Small, uncharged molecules, such as water, oxygen, carbon dioxide Ions (small, charged molecules) and large molecules (amino acids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, large lipids) cannot pass through easily SIMPLE DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION: Just like simple diffusion except particles are helped across the membrane by a carrier protein Used for larger molecules that can’t fit through the membrane Continues until dynamic equilibrium is reached Examples: Ions (small, charged molecules) Large molecules (amino acids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, large lipids) FACILITATED DIFFUSION: OSMOSIS Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from high water concentration (low solute concentration) to low water concentration (high solute concentration) Note: only the water molecules (open circles) move not the solute molecules (closed circles) ISOTONIC SOLUTION Equal concentration of solute and water inside and outside Everything is balanced and nothing moves HYPOTONIC SOLUTION Lower concentration of solute outside the cell Higher concentration of water outside the cell Water enters the cell Cell swells and bursts HYPERTONIC SOLUTION Higher concentration of solute outside of cell Lower concentration of water outside of cell Water leaves the cell Cell shrivels up ACTIVE TRANSPORT Special carriers use energy (ATP) to move chemicals across a membrane Goes against the concentration gradient Keeps going even after dynamic equilibrium is reached SODIUM-POTASSIUM PUMP An active transport mechanisms that pumps sodium and potassium ions into and out of the cell Required so that nerve and muscle cells function properly BULK TRANSPORT The movement of large quantities of materials into or out of a cell Endocytosis: A form of bulk transport used to bring large amounts of materials into the cell from the outside Two forms: Phagocytosis Pinocytosis PHAGOCYTOSIS: Also known as cell eating The bulk transport of solids into the cell PINOCYTOSIS: Also known as cell drinking The bulk transport of liquid into the cell EXOCYTOSIS: The movement of large amounts of material out of a cell FACTORS AFFECTING RATE OF DIFFUSION: Rate of diffusion depends on temperature and concentration of solute molecules in solution