* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protection against Disease
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
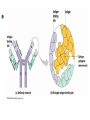
Protection against Disease Antibody Structure and Function Learning Objectives Describe structure and function of antibodies Explain the role of antibodies in immune responses Starter Activity Crossword Structure Antibodies are molecules synthesises by animals in response to the presence of a foreign substance (antigen) They are made by B lymphocytes Antibodies are proteins found in plasma, tissue fluid and milk They are also called Immunoglobins Structure They are globular proteins make up of 4 polypeptide chains- 2 light (short) MM =23000 chain and 2 heavy (long) Mm= 50-60000 chains All immunogloblins within a particular type have a similar structure for part of their molecule called the constant region. The region is highly variable. This the part that interacts with antigens The body is capable of making over million types of antibody- to counteract almost any antigen There is a 3D fit between the amino acid chain in the antibody and the antigen This is similar to that between an enzyme and substrate-although not so precise Method of Action Antibodies have 2 active sites each of which can combine with a separate antigen molecule This allows a number of antibody molecules to combine with a number of antigen molecules to form a lattice structure called an Antibody-Antigen complex The AAC immobilises virus particles so they cannot latch onto host cells The interlocking of and antibody and antigen could render a toxic antigen harmless if its active region was blocked by an antibody molecule Phagocytes can more easily track down and ingest pathogens if they are immobilised in an AAC The AAC also stimulates the activation of a number of plasma proteins. This leads to a substance called complement binding with the complex and destroying the pathogens by making cells rupture Sometimes some of the proteins cover the outer membrane of the pathogens so phagocytes can ingest them more easily. This preparation of pathogens is opsonisation Tasks